Close similarity between sequences of hepatitis E virus recovered from humans and swine, France, 2008-2009
- PMID: 22099089
- PMCID: PMC3311115
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1711.110616
Close similarity between sequences of hepatitis E virus recovered from humans and swine, France, 2008-2009
Abstract
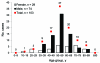
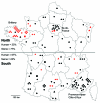
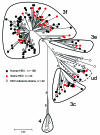
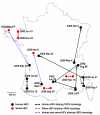
Frequent zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E virus (HEV) has been suspected, but data supporting the animal origin of autochthonous cases are still sparse. We assessed the genetic identity of HEV strains found in humans and swine during an 18-month period in France. HEV sequences identified in patients with autochthonous hepatitis E infection (n = 106) were compared with sequences amplified from swine livers collected in slaughterhouses (n = 43). Phylogenetic analysis showed the same proportions of subtypes 3f (73.8%), 3c (13.4%), and 3e (4.7%) in human and swine populations. Furthermore, similarity of >99% was found between HEV sequences of human and swine origins. These results indicate that consumption of some pork products, such as raw liver, is a major source of exposure for autochthonous HEV infection.
Figures
References
-
- Emerson SU, Anderson D, Arankalle A, Meng XJ, Purdy M, Schlauder GG, et al. Virus taxonomy VIIIth report of the ICTV. Hepevirus; 2004; 851–3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
