Enteroviruses isolated from herpangina and hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Korean children
- PMID: 22985487
- PMCID: PMC3490919
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-205
Enteroviruses isolated from herpangina and hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Korean children
Abstract
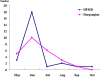
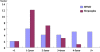
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) and herpangina are commonly prevalent illness in young children. They are similarly characterized by lesions on the skin and oral mucosa. Both diseases are associated with various enterovirus serotypes. In this study, enteroviruses from patients with these diseases in Korea in 2009 were isolated and analyzed. Demographic data for patients with HFMD and herpangina were compared and all enterovirus isolates were amplified in the VP1 region by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and sequenced. Among the enterovirus isolates, prevalent agents were coxsackievirus A16 in HFMD and coxsackievirus A5 in herpangina. More prevalent months for HFMD were June (69.2%) and May (11.5%), and June (40.0%) and July (24.0%) for herpangina. Age prevalence of HFMD patients with enterovirus infection was 1 year (23.1%), 4 years (19.2%), and over 5 years (19.2%). However, the dominant age group of herpangina patients with enterovirus infection was 1 year (48.0%) followed by 2 years (28.0%). Comparison of pairwise VP1 nucleotide sequence alignment of all isolates within the same serotypes revealed high intra-type variation of CVA2 isolates (84.6-99.3% nucleotide identity). HFMD and herpangina showed differences in demographic data and serotypes of isolated enteroviruses, but there was no notable difference in amino acid sequences by clinical syndromes in multiple comparison of the partial VP1 gene sequence.
Figures


References
-
- Bending WA, Fleming DM. Epidemiological, virological and clinical features of an epidemic of hand, food and mouth disease in England and Wales. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1996;6:R81–R86. - PubMed
-
- Rabenau HF, Richter M, Doerr HW. Hand, foot and mouth disease: seroprevalence of Coxsackie A16 and Enterovirus 71 in Germany. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2009;199:45–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

