HIV-2 integrase variation in integrase inhibitor-naïve adults in Senegal, West Africa
- PMID: 21765953
- PMCID: PMC3134476
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022204
HIV-2 integrase variation in integrase inhibitor-naïve adults in Senegal, West Africa
Abstract
Background: Antiretroviral therapy for HIV-2 infection is hampered by intrinsic resistance to many of the drugs used to treat HIV-1. Limited studies suggest that the integrase inhibitors (INIs) raltegravir and elvitegravir have potent activity against HIV-2 in culture and in infected patients. There is a paucity of data on genotypic variation in HIV-2 integrase that might confer intrinsic or transmitted INI resistance.
Methods: We PCR amplified and analyzed 122 HIV-2 integrase consensus sequences from 39 HIV-2-infected, INI-naive adults in Senegal, West Africa. We assessed genetic variation and canonical mutations known to confer INI-resistance in HIV-1.
Results: No amino acid-altering mutations were detected at sites known to be pivotal for INI resistance in HIV-1 (integrase positions 143, 148 and 155). Polymorphisms at several other HIV-1 INI resistance-associated sites were detected at positions 72, 95, 125, 154, 165, 201, 203, and 263 of the HIV-2 integrase protein.
Conclusion: Emerging genotypic and phenotypic data suggest that HIV-2 is susceptible to the new class of HIV integrase inhibitors. We hypothesize that intrinsic HIV-2 integrase variation at "secondary" HIV-1 INI-resistance sites may affect the genetic barrier to HIV-2 INI resistance. Further studies will be needed to assess INI efficacy as part of combination antiretroviral therapy in HIV-2-infected patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

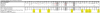
References
-
- De Cock KM, Adjorlolo G, Ekpini E, Sibailly T, Kouadio J, et al. Epidemiology and transmission of HIV-2. Why there is no HIV-2 pandemic [published erratum appears in JAMA 1994 Jan 19;271(3):196] [see comments]. JAMA. 1993;3. 270:2083–2086. - PubMed
-
- Simon F, Matheron S, Tamalet C, Loussert-Ajaka I, Bartczak S, et al. Cellular and plasma viral load in patients infected with HIV-2. AIDS. 1993;7:1411–1417. - PubMed
-
- Marlink R, Kanki P, Thior I, Travers K, Eisen G, et al. Reduced rate of disease development after HIV-2 infection as compared to HIV-1. Science. 1994;265:1587–1590. - PubMed
-
- Kanki PJ, Travers KU, MBoup S, Hsieh CC, Marlink RG, et al. Slower heterosexual spread of HIV-2 than HIV-1. Lancet. 1994;343:943–946. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb GS, Sow PS, Hawes SE, Ndoye I, Redman M, et al. Equal plasma viral loads predict a similar rate of CD4+ T cell decline in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1- and HIV-2-infected individuals from Senegal, West Africa. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:905–914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

