The C. elegans rab family: identification, classification and toolkit construction
- PMID: 23185324
- PMCID: PMC3504004
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049387
The C. elegans rab family: identification, classification and toolkit construction
Abstract
Rab monomeric GTPases regulate specific aspects of vesicle transport in eukaryotes including coat recruitment, uncoating, fission, motility, target selection and fusion. Moreover, individual Rab proteins function at specific sites within the cell, for example the ER, golgi and early endosome. Importantly, the localization and function of individual Rab subfamily members are often conserved underscoring the significant contributions that model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans can make towards a better understanding of human disease caused by Rab and vesicle trafficking malfunction. With this in mind, a bioinformatics approach was first taken to identify and classify the complete C. elegans Rab family placing individual Rabs into specific subfamilies based on molecular phylogenetics. For genes that were difficult to classify by sequence similarity alone, we did a comparative analysis of intron position among specific subfamilies from yeast to humans. This two-pronged approach allowed the classification of 30 out of 31 C. elegans Rab proteins identified here including Rab31/Rab50, a likely member of the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA). Second, a molecular toolset was created to facilitate research on biological processes that involve Rab proteins. Specifically, we used Gateway-compatible C. elegans ORFeome clones as starting material to create 44 full-length, sequence-verified, dominant-negative (DN) and constitutive active (CA) rab open reading frames (ORFs). Development of this toolset provided independent research projects for students enrolled in a research-based molecular techniques course at California State University, East Bay (CSUEB).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


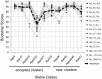
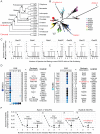
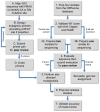

References
-
- Schwartz SL, Cao C, Pylypenko O, Rak A, Wandinger-Ness A (2008) Rab GTPases at a glance. Journal of Cell Science 121: 246–246 doi:10.1242/jcs.03495. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 513–525 doi:10.1038/nrm2728. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mitra S, Cheng KW, Mills GB (2011) Rab GTPases implicated in inherited and acquired disorders. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 22: 57–68 doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.12.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wennerberg K (2005) The Ras superfamily at a glance. Journal of Cell Science 118: 843–846 doi:10.1242/jcs.01660. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Casey PJ, Seabra MC (1996) Protein prenyltransferases. J Biol Chem 271: 5289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

