Human parainfluenza virus in patients with influenza-like illness from Central and South America during 2006-2010
- PMID: 24286248
- PMCID: PMC4186470
- DOI: 10.1111/irv.12211
Human parainfluenza virus in patients with influenza-like illness from Central and South America during 2006-2010
Abstract
Background: Human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs) are common viral causes of community-acquired pneumonia, particularly in children. The four types of HPIV have world-wide distribution; however, limited information exists about the epidemiological profile of HPIV in Latin-America.
Objective: Provide epidemiologic and phylogenetic information about HPIVs that circulated in Latin America between 2006 and 2010 to better characterize the extent and variability of this respiratory virus in the region.
Methods: Oropharyngeal swabs, demographic data and clinical characteristics were obtained from individuals with influenza-like illness in 10 Latin-American countries between 2006-2010. Specimens were analyzed with culture and molecular methods.
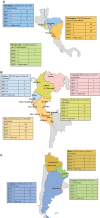
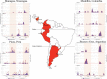
Results: A total of 30 561 individuals were enrolled; 991 (3·2%) were HPIV positive. Most infected participants were male (53·7%) and under 5 years of age (68·7%). The HPIV type most frequently isolated was HPIV-3 (403, 40·7%). In 66/2007 (3·3%) hospitalized individuals, HPIV was identified. The most frequent symptoms at enrollment were cough and rhinorrhea. We identified certain patterns for HPIV-1, -2 and -3 in specific cities. Phylogenetic analysis revealed a homogeneous distribution in the region.
Conclusions: In the current scenario, no vaccine or treatment is available for this pathogen. Our results contribute to the scarce epidemiologic and phylogenetic information of HPIV in the region that could support the development of specific management.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Latin America; parainfluenza virus; phylogenetics.
© 2013 The Authors. Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Collins PL, Chanock RM, McIntosh K. Parainfluenza viruses. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology. 3rd edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott-raven; 1996. pp. 1205–1241.
-
- Marx A, Gary HE, Jr, Marston BJ, et al. Parainfluenza virus infection among adults hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:134–140. - PubMed
-
- Denny FW, Clyde WA., Jr Acute lower respiratory tract infections in nonhospitalized children. J Pediatr. 1986;108(5 Pt 1):635–646. - PubMed
-
- Reed G, Jewett PH, Thompson J, Tollefson S, Wright PF. Epidemiology and clinical impact of parainfluenza virus infections in otherwise healthy infants and young children <5 years old. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:807–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

