Immune selection in vitro reveals human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef sequence motifs important for its immune evasion function in vivo
- PMID: 22553319
- PMCID: PMC3416312
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00878-12
Immune selection in vitro reveals human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef sequence motifs important for its immune evasion function in vivo
Abstract
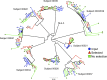
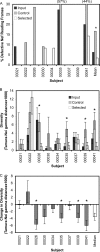
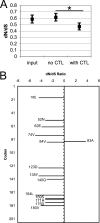
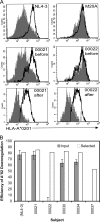
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Nef downregulates major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I), impairing the clearance of infected cells by CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). While sequence motifs mediating this function have been determined by in vitro mutagenesis studies of laboratory-adapted HIV-1 molecular clones, it is unclear whether the highly variable Nef sequences of primary isolates in vivo rely on the same sequence motifs. To address this issue, nef quasispecies from nine chronically HIV-1-infected persons were examined for sequence evolution and altered MHC-I downregulatory function under Gag-specific CTL immune pressure in vitro. This selection resulted in decreased nef diversity and strong purifying selection. Site-by-site analysis identified 13 codons undergoing purifying selection and 1 undergoing positive selection. Of the former, only 6 have been reported to have roles in Nef function, including 4 associated with MHC-I downregulation. Functional testing of naturally occurring in vivo polymorphisms at the 7 sites with no previously known functional role revealed 3 mutations (A84D, Y135F, and G140R) that ablated MHC-I downregulation and 3 (N52A, S169I, and V180E) that partially impaired MHC-I downregulation. Globally, the CTL pressure in vitro selected functional Nef from the in vivo quasispecies mixtures that predominately lacked MHC-I downregulatory function at the baseline. Overall, these data demonstrate that CTL pressure exerts a strong purifying selective pressure for MHC-I downregulation and identifies novel functional motifs present in Nef sequences in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad N, Venkatesan S. 1988. Nef protein of HIV-1 is a transcriptional repressor of HIV-1 LTR. Science 241:1481–1485 - PubMed
-
- Ali A, Jamieson BD, Yang OO. 2003. Half-genome human immunodeficiency virus type 1 constructs for rapid production of reporter viruses. J. Virol. Methods 110:137–142 - PubMed
-
- Ali A, Ng HL, Dagarag MD, Yang OO. 2005. Evasion of cytotoxic T lymphocytes is a functional constraint maintaining HIV-1 Nef expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 35:3221–3228 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

