Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel amino acid racemase, isoleucine 2-epimerase, from Lactobacillus species
- PMID: 24039265
- PMCID: PMC3811583
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00709-13
Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel amino acid racemase, isoleucine 2-epimerase, from Lactobacillus species
Abstract
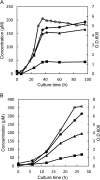
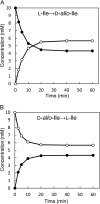
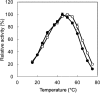
Accumulation of d-leucine, d-allo-isoleucine, and d-valine was observed in the growth medium of a lactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus otakiensis JCM 15040, and the racemase responsible was purified from the cells and identified. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the purified enzyme was GKLDKASKLI, which is consistent with that of a putative γ-aminobutyrate aminotransferase from Lactobacillus buchneri. The putative γ-aminobutyrate aminotransferase gene from L. buchneri JCM 1115 was expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli and then purified to homogeneity. The enzyme catalyzed the racemization of a broad spectrum of nonpolar amino acids. In particular, it catalyzed at high rates the epimerization of l-isoleucine to d-allo-isoleucine and d-allo-isoleucine to l-isoleucine. In contrast, the enzyme showed no γ-aminobutyrate aminotransferase activity. The relative molecular masses of the subunit and native enzyme were estimated to be about 49 kDa and 200 kDa, respectively, indicating that the enzyme was composed of four subunits of equal molecular masses. The Km and Vmax values of the enzyme for l-isoleucine were 5.00 mM and 153 μmol·min(-1)·mg(-1), respectively, and those for d-allo-isoleucine were 13.2 mM and 286 μmol·min(-1)·mg(-1), respectively. Hydroxylamine and other inhibitors of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes completely blocked the enzyme activity, indicating the enzyme requires pyridoxal 5'-phosphate as a coenzyme. This is the first evidence of an amino acid racemase that specifically catalyzes racemization of nonpolar amino acids at the C-2 position.
Figures


References
-
- Ghuysen JM. 1961. Data on the structure of disaccharide-peptide complexes liberated from the wall of Micrococcus lysodeikticus by the action of beta(1–4)N-acetylhexosaminidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 47:561–568 - PubMed
-
- Hancock R. 1960. The amino acid composition of the protein and cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 37:42–46 - PubMed
-
- Veiga P, Piquet S, Maisons A, Furlan S, Courtin P, Chapot-Chartier MP, Kulakauskas S. 2006. Identification of an essential gene responsible for D-Asp incorporation in the Lactococcus lactis peptidoglycan crossbridge. Mol. Microbiol. 62:1713–1724 - PubMed
-
- Bellais S, Arthur M, Dubost L, Hugonnet JE, Gutmann L, van Heijenoort J, Legrand R, Brouard JP, Rice L, Mainardi JL. 2006. Aslfm, the d-aspartate ligase responsible for the addition of d-aspartic acid onto the peptidoglycan precursor of Enterococcus faecium. J. Biol. Chem. 281:11586–11594 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

