Non-lethal loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay as a point-of-care diagnostics tool for Neoparamoeba perurans, the causative agent of amoebic gill disease
- PMID: 32364315
- PMCID: PMC7383609
- DOI: 10.1111/jfd.13175
Non-lethal loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay as a point-of-care diagnostics tool for Neoparamoeba perurans, the causative agent of amoebic gill disease
Abstract
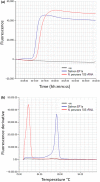
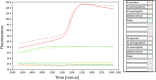
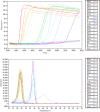
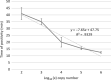
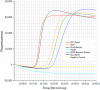
Neoparamoeba perurans is the causative agent of amoebic gill disease (AGD). Two loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays targeting the parasite 18S rRNA and the Atlantic salmon EF1α, used as internal control, were designed. The N. perurans LAMP assay did not amplify close relatives N. pemaquidensis and N. branchiphila, or the host DNA. This assay detected 106 copies of the parasite 18S rRNA gene under 13 min and 103 copies under 35 min. Five "fast-and-dirty" DNA extraction methods were compared with a reference method and further validated by TaqMan™ qPCR. Of those, the QuickExtract buffer was selected for field tests. Seventy-one non-lethal gill swabs were analysed from AGD-clinically infected Atlantic salmon. The pathogen was detected under 23 min in fish of gill score >2 and under 39 min for lower gill scores. About 1.6% of the tests were invalid (no amplification of the internal control). 100% of positives were obtained from swabs taken from fish showing gill score ˃3, but only ~50% of positives for lower gill scores. The present LAMP assay could be implemented as a point-of-care test for the on-site identification of N. perurans; however, further work is required to improve its performance for lower scores.
Keywords: Neoparamoeba perurans; amoebic gill disease; loop-mediated isothermal amplification; point-of-care test.
© 2020 Crown copyright. Journal of Fish Diseases published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. This article is published with the permission of the Controller of HMSO and the Queen’s Printer for Scotland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ball, C. S. , Light, Y. K. , Koh, C. Y. , Wheeler, S. S. , Coffey, L. L. , & Meagher, R. J. (2016). Quenching of unincorporated amplification signal reporters in reverse‐transcription loop‐mediated isothermal amplification enabling bright, single‐step, closed‐tube, and multiplexed detection of RNA viruses. Analytical Chemistry, 88(7), 3562–3568. 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04054 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baxter, E. J. , Rodger, H. D. , McAllen, R. , & Doyle, T. K. (2011). Gill disorders in marine‐farmed salmon: Investigating the role of hydrozoan jellyfish. Aquaculture Environment Interactions, 1(3), 245–257. 10.3354/aei00024 - DOI
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

