Quality of diabetes care predicts the development of cardiovascular events: results of the AMD-QUASAR study
- PMID: 21270192
- PMCID: PMC3024347
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-1709
Quality of diabetes care predicts the development of cardiovascular events: results of the AMD-QUASAR study
Abstract
Objective: The QUASAR (Quality Assessment Score and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Italian Diabetes Patients) study aimed to assess whether a quality-of-care summary score predicted the development of cardiovascular (CV) events in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: In 67 diabetes clinics, data on randomly selected patients were extracted from electronic medical records. The score was calculated using process and outcome indicators based on monitoring, targets, and treatment of A1C, blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, and microalbuminuria. The score ranged from 0 to 40.
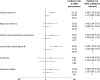
Results: Overall, 5,181 patients were analyzed; 477 (9.2%) patients developed a CV event after a median follow-up of 28 months. The incidence rate (per 1,000 person-years) of CV events was 62.4 in patients with a score of <15, 41.0 in those with a score between 20 and 25 and 36.7 in those with a score of >25. Multilevel analysis, adjusted for clustering and case-mix, showed that the risk to develop a new CV event was 84% higher in patients with a score of <15 (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.84; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.29-2.62) and 17% higher in those with a score between 15 and 25 (IRR = 1.17; 95% CI 0.93-1.49) compared with those with a score of >25. Mean quality score varied across centers from 16.5 ± 7.5 to 29.1 ± 6.3. When the score was tested as the dependent variable, it emerged that 18% of the variance in the score could be attributed to setting characteristics.
Conclusions: Our study documented a close relationship between quality of diabetes care and long-term outcomes. A simple score can be used to monitor quality of care and compare the performance of different centers/physicians.
Figures

References
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 1998;21:1414–1431 - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001;414:782–787 - PubMed
-
- Fleming BB, Greenfield S, Engelgau MM, Pogach LM, Clauser SB, Parrott MA. The Diabetes Quality Improvement Project: moving science into health policy to gain an edge on the diabetes epidemic. Diabetes Care 2001;24:1815–1820 - PubMed
-
- Smith JJ. NCQA/HEDIS guidelines for diabetes. Manag Care 2001;10(Suppl. 2):3–5 - PubMed
-
- Saaddine JB, Engelgau MM, Beckles GL, Gregg EW, Thompson TJ, Narayan KM. A diabetes report card for the United States: quality of care in the 1990s. Ann Intern Med 2002;136:565–574 - PubMed

