Isolation and characterization of a highly pathogenic strain of Porcine enteric alphacoronavirus causing watery diarrhoea and high mortality in newborn piglets
- PMID: 30103259
- PMCID: PMC7168553
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.12992
Isolation and characterization of a highly pathogenic strain of Porcine enteric alphacoronavirus causing watery diarrhoea and high mortality in newborn piglets
Abstract
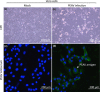
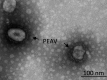
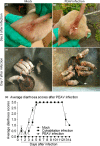
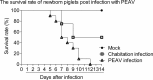
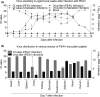
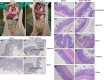
Porcine enteric alphacoronavirus (PEAV) was first discovered in China in February 2017, and the origin and virulence of this novel porcine coronavirus were not fully characterized. Here, we isolated a strain of PEAV, named GDS04 that is identified by immunofluorescence and typical crown-shaped particles observed with electron microscopy. Genomic analysis reveals that PEAV GDS04 shares a close relationship with SADS-CoV and SeACoV. Furthermore, newborn piglets orally challenged with PEAV GDS04 developed typical clinical symptoms as watery diarrhoea in neonatal piglets. Viral RNA was detected in faeces and various tissues of the infected piglets. Moreover, macroscopic and microscopic lesions in whole intestinal tract were observed, and viral antigen could be detected in the small intestines by immunohistochemical staining and electron microscopy. Importantly, the mortality rate of inoculated-newborn piglets was 100% and half of the cohabiting piglets died. Collectively, we demonstrate that PEAV is highly pathogenic in newborn piglets.
Keywords: Porcine enteric alphacoronavirus (PEAV); newborn piglets; pathogenicity.
© 2018 Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Alsaad, K. O. , Hajeer, A. H. , Al Balwi, M. , Al Moaiqel, M. , Al Oudah, N. , Al Ajlan, A. , … Arabi, Y. M. (2018). Histopathology of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronovirus (MERS‐CoV) infection ‐ clinicopathological and ultrastructural study. Histopathology, 72, 516–524. 10.1111/his.13379 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

