A GM1b/asialo-GM1 oligosaccharide-binding R-type lectin from purplish bifurcate mussels Mytilisepta virgata and its effect on MAP kinases
- PMID: 31769916
- PMCID: PMC7317968
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15154
A GM1b/asialo-GM1 oligosaccharide-binding R-type lectin from purplish bifurcate mussels Mytilisepta virgata and its effect on MAP kinases
Abstract
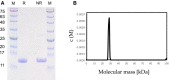
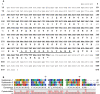
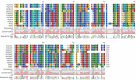
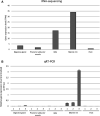
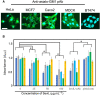
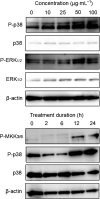
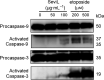
A 15-kDa lectin, termed SeviL, was isolated from Mytilisepta virgata (purplish bifurcate mussel). SeviL forms a noncovalent dimer that binds strongly to ganglio-series GM1b oligosaccharide (Neu5Acɑ2-3Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-4Glc) and its precursor, asialo-GM1 (Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-4Galβ1-4Glc). SeviL also interacts weakly with the glycan moiety of SSEA-4 hexaose (Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-3Galα1-4Galβ1-4Glc). A partial protein sequence of the lectin was determined by mass spectrometry, and the complete sequence was identified from transcriptomic analysis. SeviL, consisting of 129 amino acids, was classified as an R(icin B)-type lectin, based on the presence of the QxW motif characteristic of this fold. SeviL mRNA is highly expressed in gills and, in particular, mantle rim tissues. Orthologue sequences were identified in other species of the family Mytilidae, including Mytilus galloprovincialis, from which lectin MytiLec-1 was isolated and characterized in our previous studies. Thus, mytilid species contain lectins belonging to at least two distinct families (R-type lectins and mytilectins) that have a common β-trefoil fold structure but differing glycan-binding specificities. SeviL displayed notable cytotoxic (apoptotic) effects against various cultured cell lines (human breast, ovarian, and colonic cancer; dog kidney) that possess asialo-GM1 oligosaccharide at the cell surface. This cytotoxic effect was inhibited by the presence of anti-asialo-GM1 oligosaccharide antibodies. With HeLa ovarian cancer cells, SeviL showed dose- and time-dependent activation of kinase MKK3/6, p38 MAPK, and caspase-3/9. The transduction pathways activated by SeviL via the glycosphingolipid oligosaccharide were triggered apoptosis. DATABASE: Nucleotide sequence data have been deposited in the GenBank database under accession numbers MK434191, MK434192, MK434193, MK434194, MK434195, MK434196, MK434197, MK434198, MK434199, MK434200, and MK434201.
Keywords: Mytilisepta virgata; R-type lectin; bivalves; ganglioside; purplish bifurcate mussels.
© 2019 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rao A, Seto J, Berg JK, Kreft SG, Scheffner M & Cölfen H (2013) Roles of larval sea urchin spicule SM50 domains in organic matrix self‐assembly and calcium carbonate mineralization. J Struct Biol 183, 205–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

