Antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD in general practice: long-term impact on health-related quality of life
- PMID: 20368907
- PMCID: PMC2846154
- DOI: 10.2147/copd.s8732
Antibiotic treatment of exacerbations of COPD in general practice: long-term impact on health-related quality of life
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the impact of exacerbations in health-related quality of life (HRQL) of patients with COPD and to compare the effect of treatment of COPD exacerbations with moxifloxacin (400 mg/day for 5 days) and amoxicillin/clavulanate (500/125 mg 3 times a day for 10 days) on HRQL.
Methods: 229 outpatients with stable COPD (mean age 68.2 years; mean FEV(1) % predicted 49.3%) participated in a prospective, observational study of 2 years' duration. The St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) was completed at baseline and every 6 months thereafter.
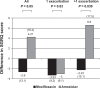
Results: COPD exacerbations (mean 2.7 episodes/patient) occurred in 136 patients (124 patients received the study medications [amoxicillin/clavulanate 54, moxifloxacin 70]). Differences between baseline and the final visit were higher for moxifloxacin compared with amoxicillin/clavulanate for total SGRQ score (-2.60 [13.1] vs 4.21 [16.2], P = 0.05) and "Symptoms" subscale (-5.64 [16.7] vs 8.27 [21], P = 0.02). The same findings were observed in patients with two or more exacerbations.
Conclusions: In COPD outpatients, treatment of exacerbations with moxifloxacin had a more favorable long-term effect on quality of life than amoxicillin/clavulanate.
Keywords: COPD; SGRQ; amoxicillin/clavulanate; exacerbations; moxifloxacin; quality of life.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman KR, Mannino DM, Soriano JB, et al. Epidemiology and costs of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:188–207. - PubMed
-
- Halpin DM, Miravitlles M. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the disease and its burden to society. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006;3:619–623. - PubMed
-
- Miravitlles M, Mayordomo C, Artés M, Sánchez-Agudo L, Nicolau F, Segú JL. Treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its exacerbations in general practice. Respir Med. 1999;93:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Miravitlles M, Murio C, Guerrero T. Factors associated with relapse after ambulatory treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Eur Respir J. 2001;17:928–933. - PubMed
-
- Miravitlles M, Guerrero T, Mayordomo C, Sánchez-Agudo L, Nicolau F, Segú JL. Factors associated with increased risk of exacerbation and hospital admission in a cohort of ambulatory COPD patients: a multiple logistic regression analysis. Respiration. 2000;67:495–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical