Reorganization of Substance Use Treatment and Harm Reduction Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Global Survey
- PMID: 34025471
- PMCID: PMC8135096
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.639393
Reorganization of Substance Use Treatment and Harm Reduction Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Global Survey
Abstract
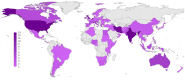
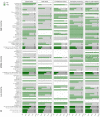
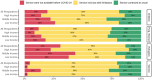
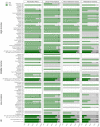
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has impacted people with substance use disorders (SUDs) worldwide, and healthcare systems have reorganized their services in response to the pandemic. Methods: One week after the announcement of the COVID-19 as a pandemic, in a global survey, 177 addiction medicine professionals described COVID-19-related health responses in their own 77 countries in terms of SUD treatment and harm reduction services. The health responses were categorized around (1) managerial measures and systems, (2) logistics, (3) service providers, and (4) vulnerable groups. Results: Respondents from over 88% of countries reported that core medical and psychiatric care for SUDs had continued; however, only 56% of countries reported having had any business continuity plan, and 37.5% of countries reported shortages of methadone or buprenorphine supplies. Participants of 41% of countries reported partial discontinuation of harm-reduction services such as needle and syringe programs and condom distribution. Fifty-seven percent of overdose prevention interventions and 81% of outreach services were also negatively impacted. Conclusions: Participants reported that SUD treatment and harm-reduction services had been significantly impacted globally early during the COVID-19 pandemic. Based on our findings, we highlight several issues and complications resulting from the pandemic concerning people with SUDs that should be tackled more efficiently during the future waves or similar pandemics. The issues and potential strategies comprise the following: (1) helping policymakers to generate business continuity plans, (2) maintaining the use of evidence-based interventions for people with SUDs, (3) being prepared for adequate medication supplies, (4) integrating harm reduction programs with other treatment modalities, and (5) having specific considerations for vulnerable groups such as immigrants and refugees.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; addiction services; drug policy; harm reduction; opioid agonist treatment; public health; substance use disorder.
Copyright © 2021 Radfar, De Jong, Farhoudian, Ebrahimi, Rafei, Vahidi, Yunesian, Kouimtsidis, Arunogiri, Massah, Deylamizadeh, Brady, Busse, ISAM-PPIG Global Survey Consortium, Potenza, Ekhtiari and Baldacchino.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

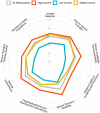
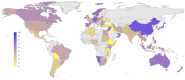
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Report No. 44 (2020).
-
- Adger WN. Social vulnerability to climate change and extremes in coastal Vietnam. World Dev. (1999) 27:249–69. 10.1016/S0305-750X00136-3 - DOI
-
- Knopf A. Addiction telemedicine comes into its own with COVID-19. Alcohol Drug Abuse Weekly. (2020) 32:5–6. 10.1002/adaw.32673 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

