In vivo electroporation enhances the immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine candidate in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 21603651
- PMCID: PMC3095594
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019252
In vivo electroporation enhances the immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine candidate in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Background: DNA-based vaccines have been safe but weakly immunogenic in humans to date.
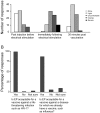
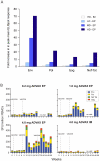
Methods and findings: We sought to determine the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of ADVAX, a multigenic HIV-1 DNA vaccine candidate, injected intramuscularly by in vivo electroporation (EP) in a Phase-1, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial in healthy volunteers. Eight volunteers each received 0.2 mg, 1 mg, or 4 mg ADVAX or saline placebo via EP, or 4 mg ADVAX via standard intramuscular injection at weeks 0 and 8. A third vaccination was administered to eleven volunteers at week 36. EP was safe, well-tolerated and considered acceptable for a prophylactic vaccine. EP delivery of ADVAX increased the magnitude of HIV-1-specific cell mediated immunity by up to 70-fold over IM injection, as measured by gamma interferon ELISpot. The number of antigens to which the response was detected improved with EP and increasing dosage. Intracellular cytokine staining analysis of ELISpot responders revealed both CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses, with co-secretion of multiple cytokines.
Conclusions: This is the first demonstration in healthy volunteers that EP is safe, tolerable, and effective in improving the magnitude, breadth and durability of cellular immune responses to a DNA vaccine candidate.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00545987.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ulmer JB, Donnelly JJ, Parker SE, Rhodes GH, Felgner PL, et al. Heterologous protection against influenza by injection of DNA encoding a viral protein. Science. 1993;259:1745–1749. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly JJ, Wahren B, Liu MA. DNA vaccines: progress and challenges. J Immunol. 2005;175(2):633–639. - PubMed
-
- Rice J, Ottensmeier CH, Stevenson FK. DNA vaccines: precision tools for activating effective immunity against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:108–120. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Doolan DL, Le TP, Hedstrom RC, Coonan KM, et al. Induction of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in humans by a malaria DNA vaccine. Science. 1998;282:476–480. - PubMed
-
- Rottinghaus ST, Poland GA, Jacobson RM, Barr LJ, Roy MJ. epatitis DNA vaccine induces protective antibody responses in human nonresponders to conventional vaccination. Vaccine. 2003;21:4604–4608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

