Familial aggregation of status epilepticus in generalized and focal epilepsies
- PMID: 32917807
- PMCID: PMC7713751
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010708
Familial aggregation of status epilepticus in generalized and focal epilepsies
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether familial aggregation of status epilepticus (SE) occurs in a large cohort of familial common epilepsies.
Methods: We used the Epilepsy Phenome/Genome Project dataset, which consisted of 2,197 participants in 1,043 family units with ≥2 members having a common generalized or nonacquired focal epilepsy (NAFE). We identified participants with a history of traditionally defined SE (TSE) (seizures ≥30 minutes) and operationally defined SE (OSE) (seizures ≥10 minutes) by chart review. We assessed familial aggregation of TSE and OSE using χ2 analysis and generalized estimating equations (GEE).
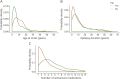
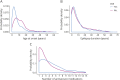
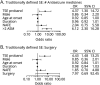
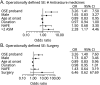
Results: One hundred fifty-five (7%) participants in 1,043 families had ≥1 episodes of TSE. Two hundred fifty (11%) had ≥1 episodes of OSE. In a χ2 analysis, the number of family units with ≥2 members having TSE (odds ratio [OR] 4.79, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.56-8.97) or OSE (OR 4.23, 95% CI 2.67-6.70) was greater than expected by chance. In GEE models adjusted for sex, broad epilepsy class (GE or NAFE), age at onset, and duration of epilepsy, TSE in a proband predicted TSE in a first-degree relative (OR 2.79, 95% CI 1.24-6.22), and OSE in a proband predicted OSE in a first-degree relative (OR 2.91, 95% CI 1.65-5.15). The results remained significant in models addressing epilepsy severity by incorporating the number of antiseizure medications used or epilepsy surgery.
Conclusions: TSE and OSE showed robust familial aggregation in a cohort of familial epilepsy independently of epilepsy severity or class, suggesting that genetic factors contribute to SE independently of the genetic cause of these epilepsies.
Clinicaltrialsgov identifier: NCT00552045.
© 2020 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Breaking up genetic influences on seizure onset, spread, and termination.Neurology. 2020 Oct 13;95(15):667-668. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000010760. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32917808 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen JW, Wasterlain CG. Status epilepticus: pathophysiology and management in adults. Lancet Neurol 2006;5:246–256. - PubMed
-
- Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, et al. . A definition and classification of status epilepticus: report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification of Status Epilepticus. Epilepsia 2015;56:1515–1523. - PubMed
-
- Dham BS, Hunter K, Rincon F. The epidemiology of status epilepticus in the United States. Neurocrit Care 2014;20:476–483. - PubMed
