Brain responses to intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet in older adults
- PMID: 38901423
- PMCID: PMC11305918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.017
Brain responses to intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet in older adults
Erratum in
-
Brain responses to intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet in older adults.Cell Metab. 2024 Aug 6;36(8):1900-1904. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.012. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 39019039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
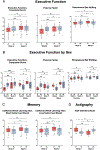
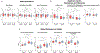
Diet may promote brain health in metabolically impaired older individuals. In an 8-week randomized clinical trial involving 40 cognitively intact older adults with insulin resistance, we examined the effects of 5:2 intermittent fasting and the healthy living diet on brain health. Although intermittent fasting induced greater weight loss, the two diets had comparable effects in improving insulin signaling biomarkers in neuron-derived extracellular vesicles, decreasing the brain-age-gap estimate (reflecting the pace of biological aging of the brain) on magnetic resonance imaging, reducing brain glucose on magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and improving blood biomarkers of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, with minimal changes in cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. Intermittent fasting and healthy living improved executive function and memory, with intermittent fasting benefiting more certain cognitive measures. In exploratory analyses, sex, body mass index, and apolipoprotein E and SLC16A7 genotypes modulated diet effects. The study provides a blueprint for assessing brain effects of dietary interventions and motivates further research on intermittent fasting and continuous diets for brain health optimization. For further information, please see ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT02460783.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarkers; brain aging; insulin resistance; intermittent fasting; randomized clinical trial.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
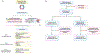

References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2022). World Population Prospects 2022: Data Sources. (UN DESA/POP/2022/DC/NO. 9).
-
- Goldstein BJ (2002). Insulin resistance as the core defect in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 90, 3G–10G. S0002914902025535 [pii]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

