A couple-based HIV prevention intervention for Latino men who have sex with men: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29622045
- PMCID: PMC5887179
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2582-y
A couple-based HIV prevention intervention for Latino men who have sex with men: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Latino men who have sex with men (MSM) experienced a 13% increase in HIV diagnoses from 2010 to 2014, more than any other racial/ethnic subgroup of MSM in the United States. If current HIV diagnoses rates persist, about one in four Latino MSM in the United States will be diagnosed with HIV during their lifetime. Although some efficacious HIV prevention interventions for Latino MSM exist, none have focused on couples. This paper describes the protocol of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) to test the preliminary efficacy of a couple-based HIV prevention intervention that is culturally tailored for Latino men and their same-sex partners.
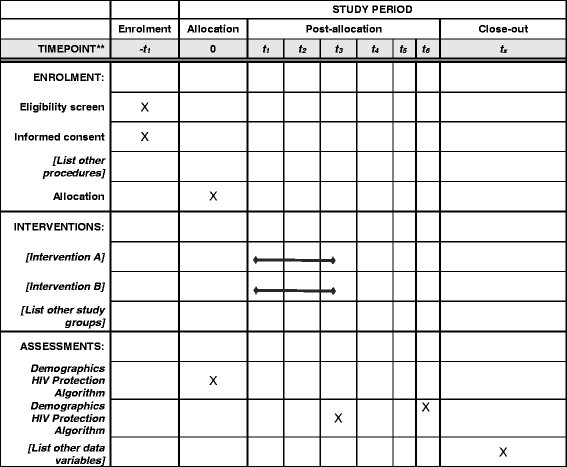
Methods: The RCT will determine the preliminary efficacy of Connecting Latinos en Pareja (CLP) to increase the proportion of anal sex acts that are HIV protected (i.e., anal sex acts in which condoms, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), treatment as prevention (TasP), or a combination thereof, are used to reduce risk of HIV transmission). CLP builds upon previous couple-based interventions with white and black MSM by incorporating biomedical prevention techniques, such as PrEP and TasP, implementing a framework responsive to the couple's serostatus, and addressing the socio-cultural factors that influence HIV risk among Latino MSM. We also include input from community stakeholders, members of the target population, and a community advisory board as part of intervention development. Assessments will be conducted at baseline, and 3- and 6-months post-intervention to examine the intervention effects on outcomes (HIV-protected sex acts), and factors potentially mediating or moderating intervention effects.
Discussion: This paper describes an innovative RCT that incorporates multiple HIV prevention techniques for Latino MSM in couples, regardless of serostatus. The ongoing involvement of community stakeholders, members of the target population, and a community advisory board is emphasized, and plans for widespread dissemination and application of findings into practice are discussed.
Trial registration: Trial registration: NCT03048838 . Registered on 3 February 2017.
Keywords: Couple-based HIV prevention intervention; HIV and AIDS; Health disparities; Implementation science.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Temple University (IRB# 24120). All participants will provide informed consent prior to participation. Any relevant changes to the protocol will be communicated to the study participants and any adverse events will be reported to the IRB (See Additional file 2 for complete informed consent).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . HIV among Hispanics/Latinos. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2016. p. 23.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Center for HIV, STD, and TB Prevention (NCHHSTP). Half of Black Gay Men and Quarter of Latino Gay Men Projected to be Diagnosed within their Lifetime. 2016.
-
- Rhodes SD, et al. Enhancement of a locally developed HIV prevention intervention for Hispanic/Latino MSM: a partnership of community-based organizations, a university, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. AIDS Educ Prev. 2015;27(4):312–332. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2015.27.4.312. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous