A Randomized, Open-Label Comparison of Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec Titration Strategies Versus Once-Daily Insulin Glargine U100
- PMID: 33875484
- PMCID: PMC8323172
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-2878
A Randomized, Open-Label Comparison of Once-Weekly Insulin Icodec Titration Strategies Versus Once-Daily Insulin Glargine U100
Abstract
Objective: Insulin icodec is a novel once-weekly basal insulin analog. This trial investigated the efficacy and safety of icodec using different once-weekly titration algorithms.
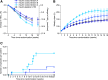
Research design and methods: This was a phase 2, randomized, open-label, 16-week, treat-to-target study. Insulin-naive adults (n = 205) with type 2 diabetes and HbA1c 7-10% while treated with oral glucose-lowering medications initiated once-weekly icodec titrations A (prebreakfast self-measured blood glucose target 80-130 mg/dL; adjustment ±21 units/week; n = 51), B (80-130 mg/dL; ±28 units/week; n = 51), or C (70-108 mg/dL; ±28 units/week; n = 52), or once-daily insulin glargine 100 units/mL (IGlar U100) (80-130 mg/dL; ±4 units/day; n = 51), all titrated weekly. Percentage of time in range (TIR) (70-180 mg/dL) during weeks 15 and 16 was measured using continuous glucose monitoring.
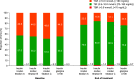
Results: TIR improved from baseline (means: A, 57.0%; B, 55.2%; C, 51.0%; IGlar U100, 55.3%) to weeks 15 and 16 (estimated mean: A, 76.6%; B, 83.0%; C, 80.9%; IGlar U100, 75.9%). TIR was greater for titration B than for IGlar U100 (estimated treatment difference 7.08%-points; 95% CI 2.12 to 12.04; P = 0.005). No unexpected safety signals were observed. Level 2 hypoglycemia (<54 mg/dL) was low in all groups (0.05, 0.15, 0.38, 0.00 events per patient-year of exposure for icodec titrations A, B, and C and IGlar U100, respectively), with no episodes of severe hypoglycemia.
Conclusions: Once-weekly icodec was efficacious and well tolerated across all three titration algorithms investigated. The results for icodec titration A (80-130 mg/dL; ±21 units/week) displayed the best balance between glycemic control and risk of hypoglycemia.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03951805.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Comment in
-
Weekly Insulin Becoming a Reality.Diabetes Care. 2021 Jul;44(7):1459-1461. doi: 10.2337/dci21-0011. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Diabetes Care. 2021. PMID: 34155035 No abstract available.
References
-
- Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Lauritzen T, et al. .; International DAWN Advisory Panel . Resistance to insulin therapy among patients and providers: results of the cross-national Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes, and Needs (DAWN) study. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2673–2679 - PubMed
-
- Yehl K. AADE practice paper in brief: diabetes educators play a critical role in successful insulin management. AADE Pract 2018;6:36–37
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

