Individualization of clinical target volume delineation in eccentric nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective comparative study
- PMID: 40831921
- PMCID: PMC12358488
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1587764
Individualization of clinical target volume delineation in eccentric nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective comparative study
Abstract
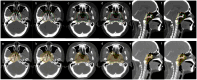
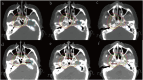
Background: Clinical target volume (CTV) delineation is a major focus in radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and currently lacks a universally accepted standard across treatment centers. We proposed an individualized CTV delineation method for eccentric NPC and evaluated its feasibility based on the eccentric distance of the primary lesion.
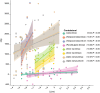
Materials and methods: Ninety patients with eccentric NPC were included. Each treatment plan was replanned using the individualized CTV method for dosimetric comparison with the conventional CTV, to evaluate coverage, homogeneity, and conformity of CTV and PTV, sparing of organs at risk (OARs) and radiotherapy technique. Paired sample t-tests and nonparametric rank-sum tests were used to compare target coverage, homogeneity, conformity, and OAR dose parameters between the two approaches. Correlation analysis is used to evaluate the correlation between eccentric distance of primary lesion and OARs dose changes. Subgroup analysis is used to compare the PTV and OARs dose parameters of individualized CTV at different T stages or radiotherapy techniques.
Results: Our results showed that compared with conventional CTV, the volume of CTV decreased significantly (P< 0.05) through individualizing delineation for eccentric NPC, especially CTV1 volume (95.81 cm³ vs. 57.57 cm³, P < 0.001). Individualized CTV reduced the doses delivered to OARs, including the brainstem, spinal cord, optic chiasm, optic nerves, and contralateral temporal lobe, inner ear and so on (all P< 0.05). When the eccentric distance of the primary lesion was between 1.4 and 2.1 cm, the individualized CTV approach provided significant advantages in organ protection, such as contralateral optic nerve, temporal lobe and parotid gland. Additionally, Subgroup analysis showed that the dose-sparing benefit of individualized CTV was more pronounced in patients treated with VMAT (volumetric modulated arc therapy).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates the dosimetric advantages of individualized CTV delineation based on eccentric distance. Our prospective trial is currently ongoing for further research (NCT06167109).
Keywords: clinical target volume; dosimetry; eccentric NPC; plan evaluation; radiotherapy techniques.
Copyright © 2025 Song, Wang, Yang, Yu, Li, Long, Shu, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Hu, Sui and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peng G, Wang T, Yang KY, Zhang S, Zhang T, Li Q, et al. A prospective, randomized study comparing outcomes and toxicities of intensity-modulated radiotherapy vs. conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. (2012) 104:286–93. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.013 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

