PLA2G6 mutation underlies infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy
- PMID: 17033970
- PMCID: PMC1698558
- DOI: 10.1086/508572
PLA2G6 mutation underlies infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy
Abstract
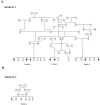
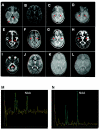
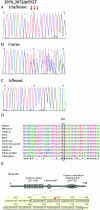
Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) is an autosomal recessive progressive neurodegenerative disease that presents within the first 2 years of life and culminates in death by age 10 years. Affected individuals from two unrelated Bedouin Israeli kindreds were studied. Brain imaging demonstrated diffuse cerebellar atrophy and abnormal iron deposition in the medial and lateral globus pallidum. Progressive white-matter disease and reduction of the N-acetyl aspartate : chromium ratio were evident on magnetic resonance spectroscopy, suggesting loss of myelination. The clinical and radiological diagnosis of INAD was verified by sural nerve biopsy. The disease gene was mapped to a 1.17-Mb locus on chromosome 22q13.1 (LOD score 4.7 at recombination fraction 0 for SNP rs139897), and an underlying mutation common to both affected families was identified in PLA2G6, the gene encoding phospholipase A2 group VI (cytosolic, calcium-independent). These findings highlight a role of phospholipase in neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures

References
Web Resources
-
- Entrez Protein, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=Protein (for PLA2 group VI, cytosolic, calcium-independent [accession number NP_003551.2])
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PANK2 cDNA [accession number NM _153640] and PLA2G6 cDNA [accession number NM_003560.2])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for INAD, PANK2, and PLA2G6)
-
- Tandem Repeats Finder, http://tandem.bu.edu/trf/trf.html
References
-
- Nardocci N, Zorzi G, Farina L, Binelli S, Scaioli W, Ciano C, Verga L, Angelini L, Savoiardo M, Bugiani O (1999) Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy: clinical spectrum and diagnostic criteria. Neurology 52:1472–1478 - PubMed
-
- Aicardi J, Castelein P (1979) Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Brain 102:727–748 - PubMed
-
- Hortnagel K, Nardocci N, Zorzi G, Garavaglia B, Botz E, Meitinger T, Klopstock T (2004) Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: locus heterogeneity. Neurology 63:922–924 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

