Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is required for normal development of skin and thymus
- PMID: 17002498
- PMCID: PMC1564426
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020146
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) is required for normal development of skin and thymus
Abstract
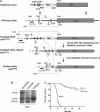
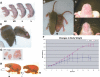
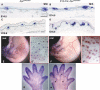
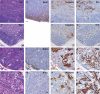
The tumor suppressor gene Apc (adenomatous polyposis coli) is a member of the Wnt signaling pathway that is involved in development and tumorigenesis. Heterozygous knockout mice for Apc have a tumor predisposition phenotype and homozygosity leads to embryonic lethality. To understand the role of Apc in development we generated a floxed allele. These mice were mated with a strain carrying Cre recombinase under the control of the human Keratin 14 (K14) promoter, which is active in basal cells of epidermis and other stratified epithelia. Mice homozygous for the floxed allele that also carry the K14-cre transgene were viable but had stunted growth and died before weaning. Histological and immunochemical examinations revealed that K14-cre-mediated Apc loss resulted in aberrant growth in many ectodermally derived squamous epithelia, including hair follicles, teeth, and oral and corneal epithelia. In addition, squamous metaplasia was observed in various epithelial-derived tissues, including the thymus. The aberrant growth of hair follicles and other appendages as well as the thymic abnormalities in K14-cre; Apc(CKO/CKO) mice suggest the Apc gene is crucial in embryonic cells to specify epithelial cell fates in organs that require epithelial-mesenchymal interactions for their development.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A. WNT and beta-catenin signalling: Diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:691–701. - PubMed
-
- Nathke IS. The adenomatous polyposis coli protein: the Achilles heel of the gut epithelium. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:337–366. - PubMed
-
- Fodde R. The multiple functions of tumour suppressors: It's all in APC. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:190–192. - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 1996;87:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, et al. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991;66:589–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

