Loss of Aire-dependent thymic expression of a peripheral tissue antigen renders it a target of autoimmunity
- PMID: 17360567
- PMCID: PMC1838644
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700259104
Loss of Aire-dependent thymic expression of a peripheral tissue antigen renders it a target of autoimmunity
Abstract
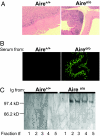
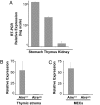
Both humans and mice with a mutation in the autoimmune regulator (aire) gene develop multiorgan autoimmune disease. Aire was shown to exert its critical function in medullary epithelial cells of the thymus by promoting ectopic expression of peripheral tissue antigens. It was hypothesized that the widespread autoimmunity of Aire-deficient individuals reflects a lack of tolerance induction to the repertoire of peripheral tissue antigens expressed in the thymus of normal individuals. Here, we substantiate this hypothesis by identifying Mucin 6 as a stomach-specific antigen targeted by autoantibodies in gastritis-prone mice lacking thymic expression of aire and demonstrate that transcription of the Mucin 6 gene in thymic medullary epithelial cells is indeed Aire-dependent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alferink J, Aigner S, Reibke R, Hammerling GJ, Arnold B. Immunol Rev. 1999;169:255–261. - PubMed
-
- Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Ann Rev Immunol. 2003;21:139–176. - PubMed
-
- Palmer E. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:383–391. - PubMed
-
- Walker LS, Abbas AK. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Ohashi PS. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15:668–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

