Control of apoptosis by asymmetric cell division
- PMID: 18399720
- PMCID: PMC2288629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060084
Control of apoptosis by asymmetric cell division
Abstract
Asymmetric cell division and apoptosis (programmed cell death) are two fundamental processes that are important for the development and function of multicellular organisms. We have found that the processes of asymmetric cell division and apoptosis can be functionally linked. Specifically, we show that asymmetric cell division in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is mediated by a pathway involving three genes, dnj-11 MIDA1, ces-2 HLF, and ces-1 Snail, that directly control the enzymatic machinery responsible for apoptosis. Interestingly, the MIDA1-like protein GlsA of the alga Volvox carteri, as well as the Snail-related proteins Snail, Escargot, and Worniu of Drosophila melanogaster, have previously been implicated in asymmetric cell division. Therefore, C. elegans dnj-11 MIDA1, ces-2 HLF, and ces-1 Snail may be components of a pathway involved in asymmetric cell division that is conserved throughout the plant and animal kingdoms. Furthermore, based on our results, we propose that this pathway directly controls the apoptotic fate in C. elegans, and possibly other animals as well.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
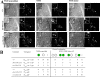
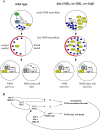
References
-
- Horvitz HR, Herskowitz I. Mechanisms of asymmetric cell division: two Bs or not two Bs, that is the question. Cell. 1992;68:237–255. - PubMed
-
- Sulston JE, Horvitz HR. Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans . Dev Biol. 1977;56:110–156. - PubMed
-
- Sulston JE, Schierenberg E, White JG, Thomson JN. The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans . Dev Biol. 1983;100:64–119. - PubMed
-
- Frank CA, Hawkins NC, Guenther C, Horvitz HR, Garriga G. C. elegans HAM-1 positions the cleavage plane and regulates apoptosis in asymmetric neuroblast divisions. Dev Biol. 2005;284:301–310. - PubMed
-
- Cordes S, Frank CA, Garriga G. The C. elegans MELK ortholog PIG-1 regulates cell size asymmetry and daughter cell fate in asymmetric neuroblast divisions. Development. 2006;133:2747–2756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

