Autosomal dominant craniometaphyseal dysplasia is caused by mutations in the transmembrane protein ANK
- PMID: 11326338
- PMCID: PMC1226118
- DOI: 10.1086/320612
Autosomal dominant craniometaphyseal dysplasia is caused by mutations in the transmembrane protein ANK
Abstract
Craniometaphyseal dysplasia (CMD) is a rare skeletal disorder characterized by progressive thickening and increased mineral density of craniofacial bones and abnormally developed metaphyses in long bones. Linkage studies mapped the locus for the autosomal dominant form of CMD to an approximately 5-cM interval on chromosome 5p, which is defined by recombinations between loci D5S810 and D5S1954. Mutational analysis of positional candidate genes was performed, and we describe herein three different mutations, in five different families and in isolated cases, in ANK, a multipass transmembrane protein involved in the transport of intracellular pyrophosphate into extracellular matrix. The mutations are two in-frame deletions and one in-frame insertion caused by a splicing defect. All mutations cluster within seven amino acids in one of the six possible cytosolic domains of ANK. These results suggest that the mutated protein has a dominant negative effect on the function of ANK, since reduced levels of pyrophosphate in bone matrix are known to increase mineralization.
Figures
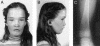
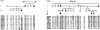

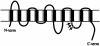
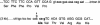
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Celera, http://www.celera.com/
-
- FACES: The National Craniofacial Association, http://www.faces-cranio.org/
-
- Genome Database, http://gdbwww.gdb.org/
-
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Sequence Archive, http://www-hgc.lbl.gov/seq/
References
-
- Balemans W, Ebeling M, Patel N, Van Hul E, Olson P, Dioszegi M, Lacza C, Wuyts W, Van Den Ende J, Willems P, Paes-Alves AF, Hill S, Bueno M, Ramos FJ, Tacconi P, Dikkers FG, Stratakis C, Lindpaintner K, Vickery B, Foernzler D, Van Hul W (2001) Increased bone density in sclerosteosis is due to the deficiency of a novel secreted protein (SOST). Hum Mol Genet 10:537–543 - PubMed
-
- Brunkow ME, Gardner JC, Van Ness J, Paeper BW, Kovacevich BR, Proll S, Skonier JE, Zhao L, Sabo PJ, Fu YH, Alisch RS, Gillett L, Colbert T, Tacconi P, Galas D, Hamersma H, Beighton P, Mulligan JT (2001) Bone dysplasia sclerosteosis results from loss of the SOST gene product, a novel cystine knot-containing protein. Am J Hum Genet 68:577–589 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caswell AM, Whyte MP, Russell RG (1991) Hypophosphatasia and the extracellular metabolism of inorganic pyrophosphate: clinical and laboratory aspects. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 28:175–232 - PubMed
-
- Chan D, Cole WG (1991) Low basal transcription of genes for tissue-specific collagens by fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells: application to the characterization of a glycine 997 to serine substitution in α 1(II) collagen chains of a patient with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. J Biol Chem 266:12487–12494 - PubMed
-
- Church DM, Yang J, Bocian M, Shiang R, Wasmuth JJ (1997) A high-resolution physical and transcript map of the Cri du chat region of human chromosome 5p. Genome Res 7:787–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

