Seven regions of the genome show evidence of linkage to type 1 diabetes in a consensus analysis of 767 multiplex families
- PMID: 11507694
- PMCID: PMC1226067
- DOI: 10.1086/323501
Seven regions of the genome show evidence of linkage to type 1 diabetes in a consensus analysis of 767 multiplex families
Abstract
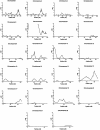
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a genetically complex disorder of glucose homeostasis that results from the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-secreting cells of the pancreas. Two previous whole-genome scans for linkage to T1D in 187 and 356 families containing affected sib pairs (ASPs) yielded apparently conflicting results, despite partial overlap in the families analyzed. However, each of these studies individually lacked power to detect loci with locus-specific disease prevalence/sib-risk ratios (lambda(s)) <1.4. In the present study, a third genome scan was performed using a new collection of 225 multiplex families with T1D, and the data from all three of these genome scans were merged and analyzed jointly. The combined sample of 831 ASPs, all with both parents genotyped, provided 90% power to detect linkage for loci with lambda(s) = 1.3 at P=7.4x10(-4). Three chromosome regions were identified that showed significant evidence of linkage (P<2.2x10(-5); LOD scores >4), 6p21 (IDDM1), 11p15 (IDDM2), 16q22-q24, and four more that showed suggestive evidence (P<7.4x10(-4), LOD scores > or =2.2), 10p11 (IDDM10), 2q31 (IDDM7, IDDM12, and IDDM13), 6q21 (IDDM15), and 1q42. Exploratory analyses, taking into account the presence of specific high-risk HLA genotypes or affected sibs' ages at disease onset, provided evidence of linkage at several additional sites, including the putative IDDM8 locus on chromosome 6q27. Our results indicate that much of the difficulty in mapping T1D susceptibility genes results from inadequate sample sizes, and the results point to the value of future international collaborations to assemble and analyze much larger data sets for linkage in complex diseases.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Institute, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics (for genotyping of families from the HBDI repository)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance of Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for T1D [MIM 222100], HLA-DQB1 [MIM 604305], HLA-DRB1 [MIM 142857], HLA-DPB1 [MIM 142858], IDDM2 [MIM 125852], IDDM3 [MIM 600318] IDDM4 [MIM 600319], IDDM5 [MIM 600320], IDDM6 [MIM 601941], IDDM7 [MIM 600321], IDDM8 [MIM 600883], IDDM10 [MIM 601942], IDDM11 [MIM 601208], IDDM12 [MIM 601388], IDDM13 [MIM 601318], IDDM 15 [MIM 601666], and IDDM18 [MIM 605598])
References
-
- Bain SC, Todd JA, Barnett AH (1990) The British Diabetic Association—Warren repository. Autoimmunity 7:83–85 - PubMed
-
- Bell GI, Horita S, Karam JH (1984) A polymorphic locus near the human insulin gene is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 33:176–183 - PubMed
-
- Bennett ST, Lucassen AM, Gough SC, Powell EE, Undlien DE, Pritchard LE, Merriman ME, Kawaguchi Y, Dronsfield MJ, Pociot F, Nerup J, Bouzekri N, Cambon-Thomsen A, Ronningen KS, Barnett AH, Bain SC, Todd JA (1995) Susceptibility to human type 1 diabetes at IDDM2 is determined by tandem repeat variation at the insulin gene minisatellite locus. Nat Genet 9:284–292 - PubMed
-
- Concannon P, Gogolin-Ewens KJ, Hinds D, Wapelhorst B, Morrison VA, Stirling B, Mitra M, Farmer J, Williams SR, Cox NJ, Bell GI, Risch N, Spielman RS (1998) A second-generation screen of the human genome for susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Nat Genet 19:292–296 - PubMed
-
- Copeman JB, Cucca F, Hearne CM, Cornall RJ, Reed PW, Ronningen KS, Undlien DE, Nistico L, Buzzetti R, Tosi R, Pociot F, Nerup J, Cornelis F, Barnett AH, Bain SC, Todd JA (1995) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility gene (IDDM7) to chromosome 2q31-q33. Nat Genet 9:80–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

