Mapping of the laminin-binding site of the N-terminal agrin domain (NtA)
- PMID: 12554653
- PMCID: PMC140726
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg041
Mapping of the laminin-binding site of the N-terminal agrin domain (NtA)
Abstract
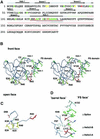
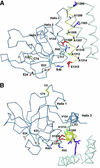
Agrin is a key organizer of acetylcholine receptor (AChR) clustering at the neuromuscular junction. The binding of agrin to laminin is required for its localization to synaptic basal lamina and other basement membranes. The high-affinity interaction with the coiled-coil domain of laminin is mediated by the N-terminal domain of agrin. We have adopted a structurally guided site-directed mutagenesis approach to map the laminin-binding site of NtA. Mutations of L117 and V124 in the C-terminal helix 3 showed that they are crucial for binding. Both residues are located in helix 3 and face the groove between the beta-barrel and the C-terminal helical segment of NtA. Remarkably, the distance between both residues matches a heptad repeat distance of two aliphatic residues which are solvent exposed in the coiled-coil domain of laminin. A lower but significant contribution originates from R43 and a charged cluster (E23, E24 and R40) at the open face of the beta-barrel structure. We propose that surface-exposed, conserved residues of the laminin gamma1 chain interact with NtA via hydrophobic and ionic interactions.
Figures






References
-
- Beck K., Hunter,I. and Engel,J. (1990) Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J., 4, 148–160. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T. et al. (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D, 54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Burgess R.W., Nguyen,Q.T., Son,Y.J., Lichtman,J.W. and Sanes,J.R. (1999) Alternatively spliced isoforms of nerve- and muscle-derived agrin: their roles at the neuromuscular junction. Neuron, 23, 33–44. - PubMed
-
- Burkin D.J., Kim,J.E., Gu,M. and Kaufman,S.J. (2000) Laminin and α7β1 integrin regulate agrin-induced clustering of acetylcholine receptors. J. Cell Sci., 113, 2877–2886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

