The crystal structure of a tetrameric hemoglobin in a partial hemichrome state
- PMID: 12093902
- PMCID: PMC125021
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.132182099
The crystal structure of a tetrameric hemoglobin in a partial hemichrome state
Abstract
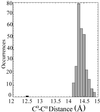
Tetrameric hemoglobins are the most widely used systems in studying protein cooperativity. Allosteric effects in hemoglobins arise from the switch between a relaxed (R) state and a tense (T) state occurring upon oxygen release. Here we report the 2.0-A crystal structure of the main hemoglobin component of the Antarctic fish Trematomus newnesi, in a partial hemichrome form. The two alpha-subunit iron atoms are bound to a CO molecule, whereas in the beta subunits the distal histidine residue is the sixth ligand of the heme iron. This structure, a tetrameric hemoglobin in the hemichrome state, demonstrates that the iron coordination by the distal histidine, usually associated with denaturing states, may be tolerated in a native-like hemoglobin structure. In addition, several features of the tertiary and quaternary organization of this structure are intermediate between the R and T states and agree well with the R --> T transition state properties obtained by spectroscopic and kinetic techniques. The analysis of this structure provides a detailed pathway of heme-heme communication and it indicates that the plasticity of the beta heme pocket plays a role in the R --> T transition of tetrameric hemoglobins.
Figures
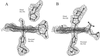
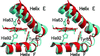
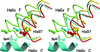
References
-
- Perutz M F. Nature (London) 1970;228:726–739. - PubMed
-
- Perutz M F, Wilkinson A J, Paoli M, Dodson G G. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:1–34. - PubMed
-
- Rifkind J M, Abugo O, Levy A, Heim J. Methods Enzymol. 1994;231:449–480. - PubMed
-
- Levy A, Rifkind J M. Biochemistry. 1985;24:6050–6054. - PubMed
-
- Levy A, Kuppusamy P, Rifkind J M. Biochemistry. 1990;29:9311–9316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

