Structure and mechanism of a coreceptor for infection by a pathogenic feline retrovirus
- PMID: 12552012
- PMCID: PMC141074
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2717-2729.2003
Structure and mechanism of a coreceptor for infection by a pathogenic feline retrovirus
Abstract
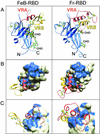
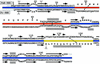
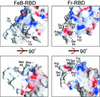
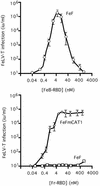
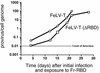
Infection of T lymphocytes by the cytopathic retrovirus feline leukemia virus subgroup T (FeLV-T) requires FeLIX, a cellular coreceptor that is encoded by an endogenous provirus and closely resembles the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of feline leukemia virus subgroup B (FeLV-B). We determined the structure of FeLV-B RBD, which has FeLIX activity, to a 2.5-A resolution by X-ray crystallography. The structure of the receptor-specific subdomain of this glycoprotein differs dramatically from that of Friend murine leukemia virus (Fr-MLV), which binds a different cell surface receptor. Remarkably, we find that Fr-MLV RBD also activates FeLV-T infection of cells expressing the Fr-MLV receptor and that FeLV-B RBD is a competitive inhibitor of infection under these conditions. These studies suggest that FeLV-T infection relies on the following property of mammalian leukemia virus RBDs: the ability to couple interaction with one of a variety of receptors to the activation of a conserved membrane fusion mechanism. A comparison of the FeLV-B and Fr-MLV RBD structures illustrates how receptor-specific regions are linked to conserved elements critical for postbinding events in virus entry.
Figures

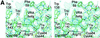

References
-
- Albritton, L. M., L. Tseng, D. Scadden, and J. M. Cunningham. 1989. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell 57:659-666. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, M. M., A. S. Lauring, C. C. Burns, and J. Overbaugh. 2000. Identification of a cellular cofactor required for infection by feline leukemia virus. Science 287:1828-1830. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

