A prion-like domain in Hsp42 drives chaperone-facilitated aggregation of misfolded proteins
- PMID: 29362223
- PMCID: PMC5881502
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201708116
A prion-like domain in Hsp42 drives chaperone-facilitated aggregation of misfolded proteins
Abstract
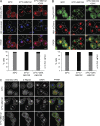
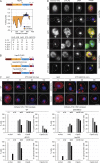
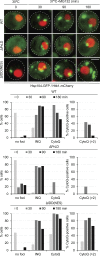
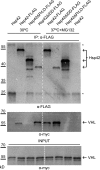
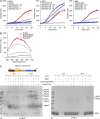
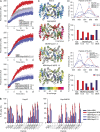
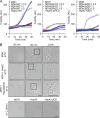
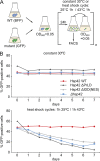
Chaperones with aggregase activity promote and organize the aggregation of misfolded proteins and their deposition at specific intracellular sites. This activity represents a novel cytoprotective strategy of protein quality control systems; however, little is known about its mechanism. In yeast, the small heat shock protein Hsp42 orchestrates the stress-induced sequestration of misfolded proteins into cytosolic aggregates (CytoQ). In this study, we show that Hsp42 harbors a prion-like domain (PrLD) and a canonical intrinsically disordered domain (IDD) that act coordinately to promote and control protein aggregation. Hsp42 PrLD is essential for CytoQ formation and is bifunctional, mediating self-association as well as binding to misfolded proteins. Hsp42 IDD confines chaperone and aggregase activity and affects CytoQ numbers and stability in vivo. Hsp42 PrLD and IDD are both crucial for cellular fitness during heat stress, demonstrating the need for sequestering misfolded proteins in a regulated manner.
© 2018 Grousl et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
One domain fits all: Using disordered regions to sequester misfolded proteins.J Cell Biol. 2018 Apr 2;217(4):1173-1175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201803015. Epub 2018 Mar 9. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29523584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cherkasov V., Grousl T., Theer P., Vainshtein Y., Glässer C., Mongis C., Kramer G., Stoecklin G., Knop M., Mogk A., and Bukau B.. 2015. Systemic control of protein synthesis through sequestration of translation and ribosome biogenesis factors during severe heat stress. FEBS Lett. 589:3654–3664. 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.10.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

