Moonlighting matrix metalloproteinase substrates: Enhancement of proinflammatory functions of extracellular tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase upon cleavage
- PMID: 31771979
- PMCID: PMC7039567
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010486
Moonlighting matrix metalloproteinase substrates: Enhancement of proinflammatory functions of extracellular tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase upon cleavage
Abstract
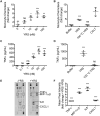
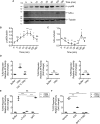
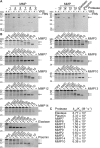
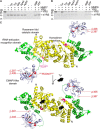
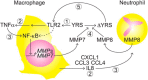
Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase ligates tyrosine to its cognate tRNA in the cytoplasm, but it can also be secreted through a noncanonical pathway. We found that extracellular tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (YRS) exhibited proinflammatory activities. In addition to acting as a monocyte/macrophage chemoattractant, YRS initiated signaling through Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) resulting in NF-κB activation and release of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and multiple chemokines, including MIP-1α/β, CXCL8 (IL8), and CXCL1 (KC) from THP1 monocyte and peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages. Furthermore, YRS up-regulated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity in a TNFα-dependent manner in M0 macrophages. Because MMPs process a variety of intracellular proteins that also exhibit extracellular moonlighting functions, we profiled 10 MMPs for YRS cleavage and identified 55 cleavage sites by
Keywords: aminoacyl tRNA synthetase; inflammation; innate immunity; macrophage; matrix metalloproteinase (MMP); moonlighting proteins; multifunctional protein; proteolysis; toll-like receptor (TLR).
© 2020 Jobin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions

