Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cytidine triphosphate synthetase, a nucleotide-regulated glutamine amidotransferase/ATP-dependent amidoligase fusion protein and homologue of anticancer and antiparasitic drug targets
- PMID: 15157079
- PMCID: PMC2891762
- DOI: 10.1021/bi0496945
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli cytidine triphosphate synthetase, a nucleotide-regulated glutamine amidotransferase/ATP-dependent amidoligase fusion protein and homologue of anticancer and antiparasitic drug targets
Abstract
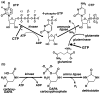
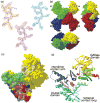
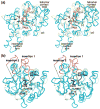
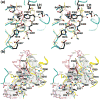
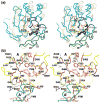
Cytidine triphosphate synthetases (CTPSs) produce CTP from UTP and glutamine, and regulate intracellular CTP levels through interactions with the four ribonucleotide triphosphates. We solved the 2.3-A resolution crystal structure of Escherichia coli CTPS using Hg-MAD phasing. The structure reveals a nearly symmetric 222 tetramer, in which each bifunctional monomer contains a dethiobiotin synthetase-like amidoligase N-terminal domain and a Type 1 glutamine amidotransferase C-terminal domain. For each amidoligase active site, essential ATP- and UTP-binding surfaces are contributed by three monomers, suggesting that activity requires tetramer formation, and that a nucleotide-dependent dimer-tetramer equilibrium contributes to the observed positive cooperativity. A gated channel that spans 25 A between the glutamine hydrolysis and amidoligase active sites provides a path for ammonia diffusion. The channel is accessible to solvent at the base of a cleft adjoining the glutamine hydrolysis active site, providing an entry point for exogenous ammonia. Guanine nucleotide binding sites of structurally related GTPases superimpose on this cleft, providing insights into allosteric regulation by GTP. Mutations that confer nucleoside drug resistance and release CTP inhibition map to a pocket that neighbors the UTP-binding site and can accommodate a pyrimidine ring. Its location suggests that competitive feedback inhibition is affected via a distinct product/drug binding site that overlaps the substrate triphosphate binding site. Overall, the E. coli structure provides a framework for homology modeling of other CTPSs and structure-based design of anti-CTPS therapeutics.
Figures


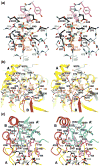
References
-
- Liebermann I. Enzymatic Amination of uridine triphosphate to cytidine triphosphate. J Am Chem Soc. 1955;55:2661–2662. - PubMed
-
- Jones ME. Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis in animals: genes, enzymes, and regulation of UMP biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:253–279. - PubMed
-
- Kent C, Carman GM, Spence MW, Dowhan W. Regulation of eukaryotic phospholipid metabolism. FASEB J. 1991;5:2258–2266. - PubMed
-
- Kent C, Carman GM. Interactions among pathways for phosphatidylcholine metabolism, CTP synthesis and secretion through the Golgi apparatus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:146–150. - PubMed
-
- West TP, O’Donovan GA. Repression of cytidine triphosphate synthetase in Salmonella typhimurium by pyrimidines during uridine nucleotide depletion. J Gen Microbiol. 1982;128:895–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

