Structure and DNA-binding properties of the cytolysin regulator CylR2 from Enterococcus faecalis
- PMID: 15359276
- PMCID: PMC517608
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600367
Structure and DNA-binding properties of the cytolysin regulator CylR2 from Enterococcus faecalis
Abstract
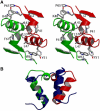
Enterococcus faecalis is one of the major causes for hospital-acquired antibiotic-resistant infections. It produces an exotoxin, called cytolysin, which is lethal for a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria and is toxic to higher organisms. Recently, the regulation of the cytolysin operon was connected to autoinduction by a quorum-sensing mechanism involving the CylR1/CylR2 two-component regulatory system. We report here the crystal structure of CylR2 and its properties in solution as determined by heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. The structure reveals a rigid dimer containing a helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif as part of a five-helix bundle that is extended by an antiparallel beta-sheet. We show that CylR2 is a DNA-binding protein that binds specifically to a 22 bp fragment of the cytolysin promoter region. NMR chemical shift perturbation experiments identify surfaces involved in DNA binding and are in agreement with a model for the CylR2/DNA complex that attributes binding specificity to a complex network of CylR2/DNA interactions. Our results propose a mechanism where repression is achieved by CylR2 obstruction of the promoter preventing biosynthesis of the cytolysin operon transcript.
Figures









References
-
- Aggarwal AK, Rodgers DW, Drottar M, Ptashne M, Harrison SC (1988) Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science 242: 899–907 - PubMed
-
- Bax A, Grzesiek S (1993) Methodological advances in protein NMR. Accounts Chem Res 26: 131–138
-
- Bell AC, Koudelka GB (1993) Operator sequence context influences amino acid–base-pair interactions in 434 repressor–operator complexes. J Mol Biol 234: 542–553 - PubMed
-
- Booth MC, Bogie CP, Sahl HG, Siezen RJ, Hatter KL, Gilmore MS (1996) Structural analysis and proteolytic activation of Enterococcus faecalis cytolysin, a novel lantibiotic. Mol Microbiol 21: 1175–1184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

