A syn-anti conformational difference allows SRSF2 to recognize guanines and cytosines equally well
- PMID: 22002536
- PMCID: PMC3252578
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.367
A syn-anti conformational difference allows SRSF2 to recognize guanines and cytosines equally well
Abstract
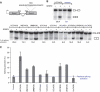
SRSF2 (SC35) is a key player in the regulation of alternative splicing events and binds degenerated RNA sequences with similar affinity in nanomolar range. We have determined the solution structure of the SRSF2 RRM bound to the 5'-UCCAGU-3' and 5'-UGGAGU-3' RNA, both identified as SRSF2 binding sites in the HIV-1 tat exon 2. RNA recognition is achieved through a novel sandwich-like structure with both termini forming a positively charged cavity to accommodate the four central nucleotides. To bind both RNA sequences equally well, SRSF2 forms a nearly identical network of intermolecular interactions by simply flipping the bases of the two consecutive C or G nucleotides into either anti or syn conformation. We validate this unusual mode of RNA recognition functionally by in-vitro and in-vivo splicing assays and propose a 5'-SSNG-3' (S=C/G) high-affinity binding consensus sequence for SRSF2. In conclusion, in addition to describe for the first time the RNA recognition mode of SRSF2, we provide the precise consensus sequence to identify new putative binding sites for this splicing factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

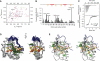
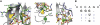
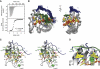

References
-
- Allain FH, Gubser CC, Howe PW, Nagai K, Neuhaus D, Varani G (1996) Specificity of ribonucleoprotein interaction determined by RNA folding during complex formulation. Nature 380: 646–650 - PubMed
-
- Arrisi-Mercado P, Romano M, Muro AF, Baralle FE (2004) An exonic splicing enhancer offsets the atypical GU-rich 3′ splice site of human apolipoprotein A-II exon 3. J Biol Chem 279: 39331–39339 - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2007) Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 663–672 - PubMed
-
- Barash Y, Calarco JA, Gao W, Pan Q, Wang X, Shai O, Blencowe BJ, Frey BJ (2010) Deciphering the splicing code. Nature 465: 53–59 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

