Structure of the N-terminal fragment of topoisomerase V reveals a new family of topoisomerases
- PMID: 16395333
- PMCID: PMC1383508
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600922
Structure of the N-terminal fragment of topoisomerase V reveals a new family of topoisomerases
Abstract
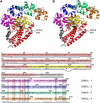
Topoisomerases are involved in controlling and maintaining the topology of DNA and are present in all kingdoms of life. Unlike all other types of topoisomerases, similar type IB enzymes have only been identified in bacteria and eukarya. The only putative type IB topoisomerase in archaea is represented by Methanopyrus kandleri topoisomerase V. Despite several common functional characteristics, topoisomerase V shows no sequence similarity to other members of the same type. The structure of the 61 kDa N-terminal fragment of topoisomerase V reveals no structural similarity to other topoisomerases. Furthermore, the structure of the active site region is different, suggesting no conservation in the cleavage and religation mechanism. Additionally, the active site is buried, indicating the need of a conformational change for activity. The presence of a topoisomerase in archaea with a unique structure suggests the evolution of a separate mechanism to alter DNA.
Figures
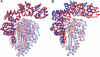




References
-
- Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Balaji S, Babu MM, Iyer LM (2005) The many faces of the helix–turn–helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29: 231–262 - PubMed
-
- Belova GI, Prasad R, Nazimov IV, Wilson SH, Slesarev AI (2002) The domain organization and properties of individual domains of DNA topoisomerase V, a type 1B topoisomerase with DNA repair activities. J Biol Chem 277: 4959–4965 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

