Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex: quinone analogue inhibitors as ligands of heme cn
- PMID: 17498743
- PMCID: PMC1993820
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.011
Structure of the cytochrome b6f complex: quinone analogue inhibitors as ligands of heme cn
Abstract
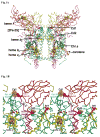
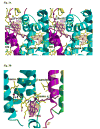
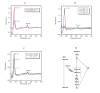
A native structure of the cytochrome b(6)f complex with improved resolution was obtained from crystals of the complex grown in the presence of divalent cadmium. Two Cd(2+) binding sites with different occupancy were determined: (i) a higher affinity site, Cd1, which bridges His143 of cytochrome f and the acidic residue, Glu75, of cyt b(6); in addition, Cd1 is coordinated by 1-2 H(2)O or 1-2 Cl(-); (ii) a second site, Cd2, of lower affinity for which three identified ligands are Asp58 (subunit IV), Glu3 (PetG subunit) and Glu4 (PetM subunit). Binding sites of quinone analogue inhibitors were sought to map the pathway of transfer of the lipophilic quinone across the b(6)f complex and to define the function of the novel heme c(n). Two sites were found for the chromone ring of the tridecyl-stigmatellin (TDS) quinone analogue inhibitor, one near the p-side [2Fe-2S] cluster. A second TDS site was found on the n-side of the complex facing the quinone exchange cavity as an axial ligand of heme c(n). A similar binding site proximal to heme c(n) was found for the n-side inhibitor, NQNO. Binding of these inhibitors required their addition to the complex before lipid used to facilitate crystallization. The similar binding of NQNO and TDS as axial ligands to heme c(n) implies that this heme utilizes plastoquinone as a natural ligand, thus defining an electron transfer complex consisting of hemes b(n), c(n), and PQ, and the pathway of n-side reduction of the PQ pool. The NQNO binding site explains several effects associated with its inhibitory action: the negative shift in heme c(n) midpoint potential, the increased amplitude of light-induced heme b(n) reduction, and an altered EPR spectrum attributed to interaction between hemes c(n) and b(n). A decreased extent of heme c(n) reduction by reduced ferredoxin in the presence of NQNO allows observation of the heme c(n) Soret band in a chemical difference spectrum.
Figures

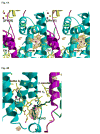
References
-
- Kallas T. The cytochrome b6f complex. In: Bryant DA, editor. The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht: 1994. pp. 259–317.
-
- O’Keefe DP. Structure and function of the chloroplast cytochrome bf complex. Photosynth Res. 1988;17:189–216. - PubMed
-
- Allen JF. Cytochrome b6f: structure for signaling and vectorial metabolism. Trends in Plant Science. 2004;9:130–137. - PubMed
-
- Kurisu G, Zhang H, Smith JL, Cramer WA. Structure and function of the cytochrome b6f complex of oxygenic photosynthesis. Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Enzymes. 2004;49:1265–1273. - PubMed
-
- Smith JL, Zhang H, Yan J, Kurisu G, Cramer WA. Cytochrome bc complexes: a common core of structure and function surrounded by diversity in the outlying provinces. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004;14:432–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

