Solution structure of the Zbeta domain of human DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors and its binding modes to B- and Z-DNAs
- PMID: 21471454
- PMCID: PMC3084098
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014898107
Solution structure of the Zbeta domain of human DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors and its binding modes to B- and Z-DNAs
Abstract
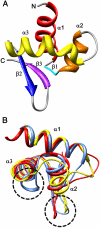
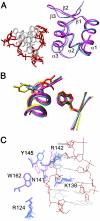
The DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors (DAI), also known as DLM-1/ZBP1, initiates an innate immune response by binding to foreign DNAs in the cytosol. For full activation of the immune response, three DNA binding domains at the N terminus are required: two Z-DNA binding domains (ZBDs), Zα and Zβ, and an adjacent putative B-DNA binding domain. The crystal structure of the Zβ domain of human DAI (hZβ(DAI)) in complex with Z-DNA revealed structural features distinct from other known Z-DNA binding proteins, and it was classified as a group II ZBD. To gain structural insights into the DNA binding mechanism of hZβ(DAI), the solution structure of the free hZβ(DAI) was solved, and its bindings to B- and Z-DNAs were analyzed by NMR spectroscopy. Compared to the Z-DNA-bound structure, the conformation of free hZβ(DAI) has notable alterations in the α3 recognition helix, the "wing," and Y145, which are critical in Z-DNA recognition. Unlike some other Zα domains, hZβ(DAI) appears to have conformational flexibility, and structural adaptation is required for Z-DNA binding. Chemical-shift perturbation experiments revealed that hZβ(DAI) also binds weakly to B-DNA via a different binding mode. The C-terminal domain of DAI is reported to undergo a conformational change on B-DNA binding; thus, it is possible that these changes are correlated. During the innate immune response, hZβ(DAI) is likely to play an active role in binding to DNAs in both B and Z conformations in the recognition of foreign DNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
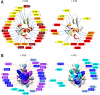
 with CG6 (Left) and hZβDAI with AT6 (Right) (α, purple, disappeared; β, blue, ≥0.10 ppm; γ, light blue, ≥0.075 ppm; δ, cyan, ≥0.05 ppm).
with CG6 (Left) and hZβDAI with AT6 (Right) (α, purple, disappeared; β, blue, ≥0.10 ppm; γ, light blue, ≥0.075 ppm; δ, cyan, ≥0.05 ppm).References
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Ishii KJ, et al. A toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:40–48. - PubMed
-
- Stetson DB, Medzhitov R. Recognition of cytosolic DNA activates an IRF3-dependent innate immune response. Immunity. 2006;24:93–103. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Nagata S. Lethal anemia caused by interferon-β produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Takaoka A, et al. DAI (DLM-1/DAI) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature. 2007;448:501–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

