Structural basis for Ca2+-induced activation and dimerization of estrogen receptor α by calmodulin
- PMID: 22275375
- PMCID: PMC3308758
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.334797
Structural basis for Ca2+-induced activation and dimerization of estrogen receptor α by calmodulin
Abstract
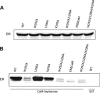
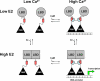
The estrogen receptor α (ER-α) regulates expression of target genes implicated in development, metabolism, and breast cancer. Calcium-dependent regulation of ER-α is critical for activating gene expression and is controlled by calmodulin (CaM). Here, we present the NMR structures for the two lobes of CaM each bound to a localized region of ER-α (residues 287-305). A model of the complete CaM·ER-α complex was constructed by combining these two structures with additional data. The two lobes of CaM both compete for binding at the same site on ER-α (residues 292, 296, 299, 302, and 303), which explains why full-length CaM binds two molecules of ER-α in a 1:2 complex and stabilizes ER-α dimerization. Exposed glutamate residues in CaM (Glu(11), Glu(14), Glu(84), and Glu(87)) form salt bridges with key lysine residues in ER-α (Lys(299), Lys(302), and Lys(303)), which are likely to prevent ubiquitination at these sites and inhibit degradation of ER-α. Mutants of ER-α at the CaM-binding site (W292A and K299A) weaken binding to CaM, and I298E/K299D disrupts estrogen-induced transcription. CaM facilitates dimerization of ER-α in the absence of estrogen, and stimulation of ER-α by either Ca(2+) and/or estrogen may serve to regulate transcription in a combinatorial fashion.
Figures

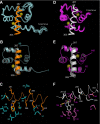
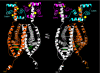
References
-
- Hall J. M., Couse J. F., Korach K. S. (2001) The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 36869–36872 - PubMed
-
- Dickson R. B., Stancel G. M. (2000) Estrogen receptor-mediated processes in normal and cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 27, 135–145 - PubMed
-
- McKenna N. J., Lanz R. B., O'Malley B. W. (1999) Nuclear receptor coregulators. Cellular and molecular biology. Endocr. Rev. 20, 321–344 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Li Z., Sacks D. B. (2005) The transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor-α is dependent on Ca2+/calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 13097–13104 - PubMed
-
- Li L., Li Z., Sacks D. B. (2003) Calmodulin regulates the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors. Selective inhibition of calmodulin function in subcellular compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 1195–1200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

