Nicotinamide riboside kinase structures reveal new pathways to NAD+
- PMID: 17914902
- PMCID: PMC1994991
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050263
Nicotinamide riboside kinase structures reveal new pathways to NAD+
Abstract
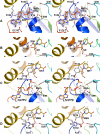
The eukaryotic nicotinamide riboside kinase (Nrk) pathway, which is induced in response to nerve damage and promotes replicative life span in yeast, converts nicotinamide riboside to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) by phosphorylation and adenylylation. Crystal structures of human Nrk1 bound to nucleoside and nucleotide substrates and products revealed an enzyme structurally similar to Rossmann fold metabolite kinases and allowed the identification of active site residues, which were shown to be essential for human Nrk1 and Nrk2 activity in vivo. Although the structures account for the 500-fold discrimination between nicotinamide riboside and pyrimidine nucleosides, no enzyme feature was identified to recognize the distinctive carboxamide group of nicotinamide riboside. Indeed, nicotinic acid riboside is a specific substrate of human Nrk enzymes and is utilized in yeast in a novel biosynthetic pathway that depends on Nrk and NAD+ synthetase. Additionally, nicotinic acid riboside is utilized in vivo by Urh1, Pnp1, and Preiss-Handler salvage. Thus, crystal structures of Nrk1 led to the identification of new pathways to NAD+.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


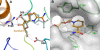

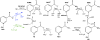
References
-
- Belenky P, Bogan KL, Brenner C. NAD(+) metabolism in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:12–19. - PubMed
-
- Krehl WA, Trepley LJ, Sarma PS, Elvehjem CA. Growth retarding effect of corn in niacin-low rations and its counteraction by tryptophan. Science. 1945;101:489–490. - PubMed
-
- Elvehjem CA, Madden RJ, Strong FM, Woolley DW. The isolation and identification of the anti-black tongue factor. J Biol Chem. 1938;123:137–149. - PubMed
-
- Bieganowski P, Brenner C. Discoveries of nicotinamide riboside as a nutrient and conserved NRK genes establish a Preiss-Handler independent route to NAD+ in fungi and humans. Cell. 2004;117:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 2000;403:795–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

