Regulation of the sigmaE stress response by DegS: how the PDZ domain keeps the protease inactive in the resting state and allows integration of different OMP-derived stress signals upon folding stress
- PMID: 17938245
- PMCID: PMC2000328
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.445307
Regulation of the sigmaE stress response by DegS: how the PDZ domain keeps the protease inactive in the resting state and allows integration of different OMP-derived stress signals upon folding stress
Abstract
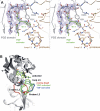
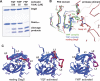
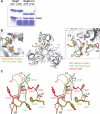
The unfolded protein response of Escherichia coli is triggered by the accumulation of unassembled outer membrane proteins (OMPs) in the cellular envelope. The PDZ-protease DegS recognizes these mislocalized OMPs and initiates a proteolytic cascade that ultimately leads to the sigmaE-driven expression of a variety of factors dealing with folding stress in the periplasm and OMP assembly. The general features of how OMPs activate the protease function of DegS have not yet been systematically addressed. Furthermore, it is unknown how the PDZ domain keeps the protease inactive in the resting state, which is of crucial importance for the functioning of the entire sigmaE stress response. Here we show in atomic detail how DegS is able to integrate the information of distinct stress signals that originate from different OMPs containing a -x-Phe C-terminal motif. A dedicated loop of the protease domain, loop L3, serves as a versatile sensor for allosteric ligands. L3 is capable of interacting differently with ligands but reorients in a conserved manner to activate DegS. Our data also indicate that the PDZ domain directly inhibits protease function in the absence of stress signals by wedging loop L3 in a conformation that ultimately disrupts the proteolytic site. Thus, the PDZ domain and loop L3 of DegS define a novel molecular switch allowing strict regulation of the sigmaE stress response system.
Figures
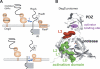

References
-
- Ades S.E., Connolly L.E., Alba B.M., Gross C.A., Connolly L.E., Alba B.M., Gross C.A., Alba B.M., Gross C.A., Gross C.A. The Escherichia coli σ(E)-dependent extracytoplasmic stress response is controlled by the regulated proteolysis of an anti-σ factor. Genes & Dev. 1999;13:2449–2461. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alba B.M., Leeds J.A., Onufryk C., Lu C.Z., Gross C.A., Leeds J.A., Onufryk C., Lu C.Z., Gross C.A., Onufryk C., Lu C.Z., Gross C.A., Lu C.Z., Gross C.A., Gross C.A. DegS and YaeL participate sequentially in the cleavage of RseA to activate the σ(E)-dependent extracytoplasmic stress response. Genes & Dev. 2002;16:2156–2168. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown M.S., Ye J., Rawson R.B., Goldstein J.L., Ye J., Rawson R.B., Goldstein J.L., Rawson R.B., Goldstein J.L., Goldstein J.L. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: A control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell. 2000;100:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams P.D., Clore G.M., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Adams P.D., Clore G.M., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Clore G.M., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Nilges M., Pannu N.S., Pannu N.S., et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
