Inhibition of the EGF receptor by binding of MIG6 to an activating kinase domain interface
- PMID: 18046415
- PMCID: PMC3561764
- DOI: 10.1038/nature05998
Inhibition of the EGF receptor by binding of MIG6 to an activating kinase domain interface
Abstract
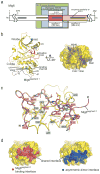
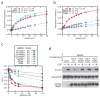
Members of the epidermal growth factor receptor family (EGFR/ERBB1, ERBB2/HER2, ERBB3/HER3 and ERBB4/HER4) are key targets for inhibition in cancer therapy. Critical for activation is the formation of an asymmetric dimer by the intracellular kinase domains, in which the carboxy-terminal lobe (C lobe) of one kinase domain induces an active conformation in the other. The cytoplasmic protein MIG6 (mitogen-induced gene 6; also known as ERRFI1) interacts with and inhibits the kinase domains of EGFR and ERBB2 (refs 3-5). Crystal structures of complexes between the EGFR kinase domain and a fragment of MIG6 show that a approximately 25-residue epitope (segment 1) from MIG6 binds to the distal surface of the C lobe of the kinase domain. Biochemical and cell-based analyses confirm that this interaction contributes to EGFR inhibition by blocking the formation of the activating dimer interface. A longer MIG6 peptide that is extended C terminal to segment 1 has increased potency as an inhibitor of the activated EGFR kinase domain, while retaining a critical dependence on segment 1. We show that signalling by EGFR molecules that contain constitutively active kinase domains still requires formation of the asymmetric dimer, underscoring the importance of dimer interface blockage in MIG6-mediated inhibition.
Figures


References
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5 (5):341–354. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, et al. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell. 2006;125 (6):1137–1149. - PubMed
-
- Hackel PO, Gishizky M, Ullrich A. Mig-6 is a negative regulator of the epidermal growth factor receptor signal. Biol Chem. 2001;382 (12):1649–1662. - PubMed
-
- Xu Dazhong, Makkinje Anthony, Kyriakis John M. Gene 33 Is an Endogenous Inhibitor of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Receptor Signaling and Mediates Dexamethasone-induced Suppression of EGF Function. J Biol Chem. 2005;280 (4):2924–2933. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

