Structure of cytochrome P450 PimD suggests epoxidation of the polyene macrolide pimaricin occurs via a hydroperoxoferric intermediate
- PMID: 20797613
- PMCID: PMC2932657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.05.026
Structure of cytochrome P450 PimD suggests epoxidation of the polyene macrolide pimaricin occurs via a hydroperoxoferric intermediate
Abstract
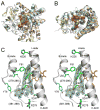
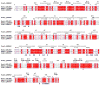
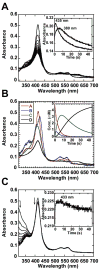
We present the X-ray structure of PimD, both substrate-free and in complex with 4,5-desepoxypimaricin. PimD is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase with native epoxidase activity that is critical in the biosynthesis of the polyene macrolide antibiotic pimaricin. Intervention in this secondary metabolic pathway could advance the development of drugs with improved pharmacologic properties. Epoxidation by P450 typically includes formation of a charge-transfer complex between an oxoferryl pi-cation radical species (Compound I) and the olefin pi-bond as the initial intermediate. Catalytic and structural evidence presented here suggest that epoxidation of 4,5-desepoxypimaricin proceeds via a hydroperoxoferric intermediate (Compound 0). The oxygen atom of Compound 0 distal to the heme iron may insert into the double bond of the substrate to make an epoxide ring. Stereoelectronic features of the putative transition state suggest substrate-assisted proton delivery.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


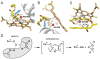

References
-
- Collaborative Computational Project Number 4. Acta Crysallogr D. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio JF, Caffrey P, Gil JA, Zotchev SB. Polyene antibiotic biosynthesis gene clusters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;61:179–188. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio JF, Mendes MV, Anton N, Recio E, Martin JF. Polyene macrolide antibiotic biosynthesis. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:1645–1656. - PubMed
-
- Bach RD, Dmitrenko O. Strain energy of small ring hydrocarbons. Influence of C-H bond dissociation energies. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:4444–4452. - PubMed
-
- Baginski M, Czub J, Sternal K. Interaction of amphotericin B and its selected derivatives with membranes: molecular modeling studies. Chem Rec. 2006;6:320–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

