Functional importance of crenarchaea-specific extra-loop revealed by an X-ray structure of a heterotetrameric crenarchaeal splicing endonuclease
- PMID: 19515941
- PMCID: PMC2724299
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp506
Functional importance of crenarchaea-specific extra-loop revealed by an X-ray structure of a heterotetrameric crenarchaeal splicing endonuclease
Abstract
Archaeal splicing endonucleases (EndAs) are currently classified into three groups. Two groups require a single subunit protein to form a homodimer or homotetramer. The third group requires two nonidentical protein components for the activity. To elucidate the molecular architecture of the two-subunit EndA system, we studied a crenarchaeal splicing endonuclease from Pyrobaculum aerophilum. In the present study, we solved a crystal structure of the enzyme at 1.7-A resolution. The enzyme adopts a heterotetrameric form composed of two catalytic and two structural subunits. By connecting the structural and the catalytic subunits of the heterotetrameric EndA, we could convert the enzyme to a homodimer that maintains the broad substrate specificity that is one of the characteristics of heterotetrameric EndA. Meanwhile, a deletion of six amino acids in a Crenarchaea-specific loop abolished the endonuclease activity even on a substrate with canonical BHB motif. These results indicate that the subunit architecture is not a major factor responsible for the difference of substrate specificity between single- and two-subunit EndA systems. Rather, the structural basis for the broad substrate specificity is built into the crenarchaeal splicing endonuclease itself.
Figures

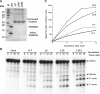

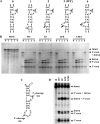

References
-
- Li H. Complexes of tRNA and maturation enzymes: shaping up for translation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007;17:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Abelson J, Trotta CR, Li H. tRNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:12685–12688. - PubMed
-
- Trotta CR, Miao F, Arn EA, Stevens SW, Ho CK, Rauhut R, Abelson JN. The yeast tRNA splicing endonuclease: a tetrameric enzyme with two active site subunits homologous to the archaeal tRNA endonucleases. Cell. 1997;89:849–858. - PubMed
-
- Di Nicola Negri E, Fabbri S, Bufardeci E, Baldi MI, Gandini Attardi D, Mattoccia E, Tocchini-Valentini GP. The eucaryal tRNA splicing endonuclease recognizes a tripartite set of RNA elements. Cell. 1997;89:859–866. - PubMed
-
- Paushkin SV, Patel M, Furia BS, Peltz SW, Trotta CR. Identification of a human endonuclease complex reveals a link between tRNA splicing and pre-mRNA 3′ end formation. Cell. 2004;117:311–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

