A molecular basis for NKT cell recognition of CD1d-self-antigen
- PMID: 21376640
- PMCID: PMC3070541
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.01.013
A molecular basis for NKT cell recognition of CD1d-self-antigen
Abstract
The antigen receptor for natural killer T cells (NKT TCR) binds CD1d-restricted microbial and self-lipid antigens, although the molecular basis of self-CD1d recognition is unclear. Here, we have characterized NKT TCR recognition of CD1d molecules loaded with natural self-antigens (Ags) and report the 2.3 Å resolution structure of an autoreactive NKT TCR-phosphatidylinositol-CD1d complex. NKT TCR recognition of self- and foreign antigens was underpinned by a similar mode of germline-encoded recognition of CD1d. However, NKT TCR autoreactivity is mediated by unique sequences within the non-germline-encoded CDR3β loop encoding for a hydrophobic motif that promotes self-association with CD1d. Accordingly, NKT cell autoreactivity may arise from the inherent affinity of the interaction between CD1d and the NKT TCR, resulting in the recognition of a broad range of CD1d-restricted self-antigens. This demonstrates that multiple self-antigens can be recognized in a similar manner by autoreactive NKT TCRs.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
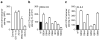


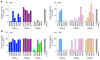
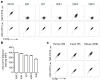
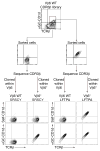
Comment in
-
The immutable recognition of CD1d.Immunity. 2011 Mar 25;34(3):281-3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.006. Immunity. 2011. PMID: 21435579
References
-
- Arden B, Clark SP, Kabelitz D, Mak TW. Mouse T-cell receptor variable gene segment families. Immunogenetics. 1995;42:501–530. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The Biology of NKT Cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Borg NA, Wun KS, Kjer-Nielsen L, Wilce MC, Pellicci DG, Koh R, Besra GS, Bharadwaj M, Godfrey DI, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J. CD1d-lipid-antigen recognition by the semi-invariant NKT T-cell receptor. Nature. 2007;448:44–49. - PubMed
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. How invariant natural killer T cells respond to infection by recognizing microbial or endogenous lipid antigens. Sem Immunol. 2009;22:79–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

