Functional anatomy of phospholipid binding and regulation of phosphoinositide homeostasis by proteins of the sec14 superfamily
- PMID: 18243114
- PMCID: PMC7808562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.026
Functional anatomy of phospholipid binding and regulation of phosphoinositide homeostasis by proteins of the sec14 superfamily
Abstract
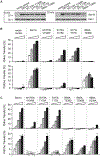
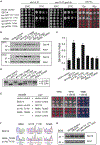
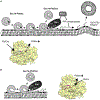
Sec14, the major yeast phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns)/phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) transfer protein, regulates essential interfaces between lipid metabolism and membrane trafficking from the trans-Golgi network (TGN). How Sec14 does so remains unclear. We report that Sec14 binds PtdIns and PtdCho at distinct (but overlapping) sites, and both PtdIns- and PtdCho-binding activities are essential Sec14 activities. We further show both activities must reside within the same molecule to reconstitute a functional Sec14 and for effective Sec14-mediated regulation of phosphoinositide homeostasis in vivo. This regulation is uncoupled from PtdIns-transfer activity and argues for an interfacial presentation mode for Sec14-mediated potentiation of PtdIns kinases. Such a regulatory role for Sec14 is a primary counter to action of the Kes1 sterol-binding protein that antagonizes PtdIns 4-OH kinase activity in vivo. Collectively, these findings outline functional mechanisms for the Sec14 superfamily and reveal additional layers of complexity for regulating phosphoinositide homeostasis in eukaryotes.
Figures




Comment in
-
The lipid trade.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;15(2):79. doi: 10.1038/nrm3740. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24434885 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Al-Aidroos K, and Bussey H (1978). Chromosomal mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae affecting the cell wall binding site for killer factor. Can. J. Microbiol 24, 228–237. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L, and Koonin EV (1999). Gleaning non-trivial structural, functional and evolutionary information about proteins by iterative database searches.J. Mol. Biol 287, 1023–1040. - PubMed
-
- Bankaitis VA, Aitken JR, Cleves AE, and Dowhan W (1990). An essential role for a PL transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature 347, 561–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

