DNA binding site sequence directs glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity
- PMID: 19372434
- PMCID: PMC2777810
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1164265
DNA binding site sequence directs glucocorticoid receptor structure and activity
Abstract
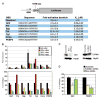
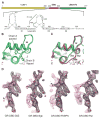
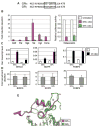
Genes are not simply turned on or off, but instead their expression is fine-tuned to meet the needs of a cell. How genes are modulated so precisely is not well understood. The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) regulates target genes by associating with specific DNA binding sites, the sequences of which differ between genes. Traditionally, these binding sites have been viewed only as docking sites. Using structural, biochemical, and cell-based assays, we show that GR binding sequences, differing by as little as a single base pair, differentially affect GR conformation and regulatory activity. We therefore propose that DNA is a sequence-specific allosteric ligand of GR that tailors the activity of the receptor toward specific target genes.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

