Transition state analogues in structures of ricin and saporin ribosome-inactivating proteins
- PMID: 19920175
- PMCID: PMC2787146
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0911606106
Transition state analogues in structures of ricin and saporin ribosome-inactivating proteins
Abstract
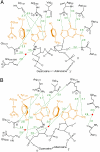
Ricin A-chain (RTA) and saporin-L1 (SAP) catalyze adenosine depurination of 28S rRNA to inhibit protein synthesis and cause cell death. We present the crystal structures of RTA and SAP in complex with transition state analogue inhibitors. These tight-binding inhibitors mimic the sarcin-ricin recognition loop of 28S rRNA and the dissociative ribocation transition state established for RTA catalysis. RTA and SAP share unique purine-binding geometry with quadruple pi-stacking interactions between adjacent adenine and guanine bases and 2 conserved tyrosines. An arginine at one end of the pi-stack provides cationic polarization and enhanced leaving group ability to the susceptible adenine. Common features of these ribosome-inactivating proteins include adenine leaving group activation, a remarkable lack of ribocation stabilization, and conserved glutamates as general bases for activation of the H(2)O nucleophile. Catalytic forces originate primarily from leaving group activation evident in both RTA and SAP in complex with transition state analogues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Endo Y, Mitsui K, Motizuki M, Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:5908–5912. - PubMed
-
- Amlot PL, et al. A phase I study of an anti-CD22-deglycosylated ricin A chain immunotoxin in the treatment of B-cell lymphomas resistant to conventional therapy. Blood. 1993;82:2624–2633. - PubMed
-
- Messmann RA, et al. A phase I study of combination therapy with immunotoxins IgG-HD37-deglycosylated ricin A chain (dgA) and IgG-RFB4-dgA (Combotox) in patients with refractory CD19(+), CD22(+) B cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1302–1313. - PubMed
-
- Sausville EA, et al. Continuous infusion of the anti-CD22 immunotoxin IgG-RFB4-SMPT-dgA in patients with B-cell lymphoma: A phase I study. Blood. 1995;85:3457–3465. - PubMed
-
- Senderowicz AM, et al. Complete sustained response of a refractory, post-transplantation, large B-cell lymphoma to an anti-CD22 immunotoxin. Ann Intern Med. 1997;126:882–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

