Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M
- PMID: 20033049
- PMCID: PMC2879581
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08622
Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M
Abstract
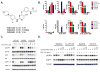
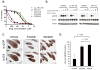
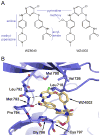
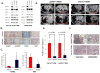
The clinical efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is limited by the development of drug-resistance mutations, including the gatekeeper T790M mutation. Strategies targeting EGFR T790M with irreversible inhibitors have had limited success and are associated with toxicity due to concurrent inhibition of wild-type EGFR. All current EGFR inhibitors possess a structurally related quinazoline-based core scaffold and were identified as ATP-competitive inhibitors of wild-type EGFR. Here we identify a covalent pyrimidine EGFR inhibitor by screening an irreversible kinase inhibitor library specifically against EGFR T790M. These agents are 30- to 100-fold more potent against EGFR T790M, and up to 100-fold less potent against wild-type EGFR, than quinazoline-based EGFR inhibitors in vitro. They are also effective in murine models of lung cancer driven by EGFR T790M. Co-crystallization studies reveal a structural basis for the increased potency and mutant selectivity of these agents. These mutant-selective irreversible EGFR kinase inhibitors may be clinically more effective and better tolerated than quinazoline-based inhibitors. Our findings demonstrate that functional pharmacological screens against clinically important mutant kinases represent a powerful strategy to identify new classes of mutant-selective kinase inhibitors.
Figures
References
-
- Mok TS, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–792. - PubMed
-
- Li D, et al. Bronchial and peripheral murine lung carcinomas induced by T790M-L858R mutant EGFR respond to HKI-272 and rapamycin combination therapy. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:81–93. - PubMed
-
- Besse B, et al. Neratinib (HKI-272), an irreversible pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibtor: preliminary results of a phase 2 tiral in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. European Journal of Cancer. 2008;6:64. abstract 203.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P50CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA116020/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM070590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM070590/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080942/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA080942/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA135257/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA130876/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG2400401/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA11446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA135257/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA130876-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA116020/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

