Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family
- PMID: 22464331
- PMCID: PMC3326523
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013
Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family
Abstract
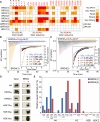
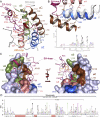
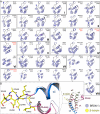
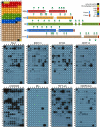
Bromodomains (BRDs) are protein interaction modules that specifically recognize ε-N-lysine acetylation motifs, a key event in the reading process of epigenetic marks. The 61 BRDs in the human genome cluster into eight families based on structure/sequence similarity. Here, we present 29 high-resolution crystal structures, covering all BRD families. Comprehensive crossfamily structural analysis identifies conserved and family-specific structural features that are necessary for specific acetylation-dependent substrate recognition. Screening of more than 30 representative BRDs against systematic histone-peptide arrays identifies new BRD substrates and reveals a strong influence of flanking posttranslational modifications, such as acetylation and phosphorylation, suggesting that BRDs recognize combinations of marks rather than singly acetylated sequences. We further uncovered a structural mechanism for the simultaneous binding and recognition of diverse diacetyl-containing peptides by BRD4. These data provide a foundation for structure-based drug design of specific inhibitors for this emerging target family.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

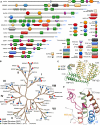
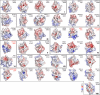

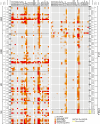
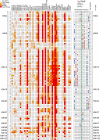




References
-
- Berger S.L. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
-
- Beyer M., Block I., König K., Nesterov A., Fernandez S., Felgenhauer T., Schirwitz C., Leibe K., Bischoff R.F., Breitling F., Stadler V. A novel combinatorial approach to high-density peptide arrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;570:309–316. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Abagyan, R., Totrov, M., and Kuznetsov, D. (1994). ICM—a new method for protein modeling and design: applications to docking and structure prediction from the distorted native conformation. J. Comput. Chem. 15, 488–506.
-
- Akai, Y., Adachi, N., Hayashi, Y., Eitoku, M., Sano, N., Natsume, R., Kudo, N., Tanokura, M., Senda, T., and Horikoshi, M. (2010). Structure of the histone chaperone CIA/ASF1-double bromodomain complex linking histone modifications and site-specific histone eviction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 8153–8158. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brand, M., Rampalli, S., Chaturvedi, C.P., and Dilworth, F.J. (2008). Analysis of epigenetic modifications of chromatin at specific gene loci by native chromatin immunoprecipitation of nucleosomes isolated using hydroxyapatite chromatography. Nat. Protoc. 3, 398–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

