Identification of the growth factor-binding sequence in the extracellular matrix protein MAGP-1
- PMID: 31988245
- PMCID: PMC7049978
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010540
Identification of the growth factor-binding sequence in the extracellular matrix protein MAGP-1
Abstract
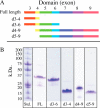
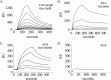
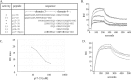
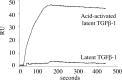
Microfibril-associated glycoprotein-1 (MAGP-1) is a component of vertebrate extracellular matrix (ECM) microfibrils that, together with the fibrillins, contributes to microfibril function. Many of the phenotypes associated with MAGP-1 gene inactivation are consistent with dysregulation of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)/bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling system. We have previously shown that full-length MAGP-1 binds active TGFβ-1 and some BMPs. The work presented here further defines the growth factor-binding domain of MAGP-1. Using recombinant domains and synthetic peptides, along with surface plasmon resonance analysis to measure the kinetics of the MAGP-1-TGFβ-1 interaction, we localized the TGFβ- and BMP-binding site in MAGP-1 to a 19-amino acid-long, highly acidic sequence near the N terminus. This domain was specific for binding active, but not latent, TGFβ-1. Growth factor activity experiments revealed that TGFβ-1 retains signaling activity when complexed with MAGP-1. Furthermore, when bound to fibrillin, MAGP-1 retained the ability to interact with TGFβ-1, and active TGFβ-1 did not bind fibrillin in the absence of MAGP-1. The absence of MAGP was sufficient to raise the amount of total TGFβ stored in the ECM of cultured cells, suggesting that the MAGPs compete with the TGFβ large latent complex for binding to microfibrils. Together, these results indicate that MAGP-1 plays an active role in TGFβ signaling in the ECM.
Keywords: MFAP2; TGFβ; bone morphogenetic protein (BMP); cell signaling; extracellular cellular matrix (ECM); extracellular matrix; fibrillar; fibrillin; growth factor; growth factor signaling; microfibril; microfibril associated glycoprotein (MAGP); protein-protein interaction; transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ).
© 2020 Broekelmann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

