The structural basis for mRNA recognition and cleavage by the ribosome-dependent endonuclease RelE
- PMID: 20005802
- PMCID: PMC2807027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.015
The structural basis for mRNA recognition and cleavage by the ribosome-dependent endonuclease RelE
Abstract
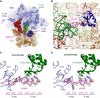
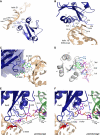
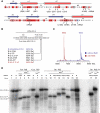
Translational control is widely used to adjust gene expression levels. During the stringent response in bacteria, mRNA is degraded on the ribosome by the ribosome-dependent endonuclease, RelE. The molecular basis for recognition of the ribosome and mRNA by RelE and the mechanism of cleavage are unknown. Here, we present crystal structures of E. coli RelE in isolation (2.5 A) and bound to programmed Thermus thermophilus 70S ribosomes before (3.3 A) and after (3.6 A) cleavage. RelE occupies the A site and causes cleavage of mRNA after the second nucleotide of the codon by reorienting and activating the mRNA for 2'-OH-induced hydrolysis. Stacking of A site codon bases with conserved residues in RelE and 16S rRNA explains the requirement for the ribosome in catalysis and the subtle sequence specificity of the reaction. These structures provide detailed insight into the translational regulation on the bacterial ribosome by mRNA cleavage.
Figures
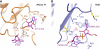

References
-
- Adams P.D., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Hung L.W., Ioerger T.R., McCoy A.J., Moriarty N.W., Read R.J., Sacchettini J.C., Sauter N.K., Terwilliger T.C. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Bauerova-Hlinkova V., Dvorsky R., Perecko D., Povazanec F., Sevcik J. Structure of RNase Sa2 complexes with mononucleotides–new aspects of catalytic reaction and substrate recognition. FEBS J. 2009;276:4156–4168. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T., Adams P.D., Clore G.M., DeLano W.L., Gros P., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Jiang J.S., Kuszewski J., Nilges M., Pannu N.S. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. - PubMed
-
- Christensen-Dalsgaard M., Gerdes K. Two higBA loci in the Vibrio cholerae superintegron encode mRNA cleaving enzymes and can stabilize plasmids. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;62:397–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

